Updated May 12, 2021
Maintenance is key to managing and optimizing manufacturing equipment and industrial assets, but implementing the right maintenance strategy is even more important.
After all, there are many types of maintenance that manufacturers can implement, each varying in the degree of difficulty and effectiveness. As manufacturers develop greater accessibility to the performance and health of their equipment, they can develop a stronger understanding of when maintenance should be performed.
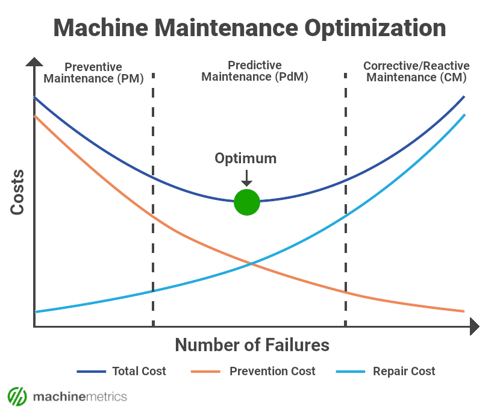
This ultimately becomes a game of weighing the costs of maintenance against the cost of machine downtimes. The happy middle ground represents a perfect combination of reduced maintenance costs and reduced downtime. However, this can be quite difficult.
As you can imagine, when reducing maintenance costs, you are likely to increase downtimes, and by reducing all your downtime, your maintenance costs are likely to rise.
This is an important distinction between predictive and preventative that we will discuss below.
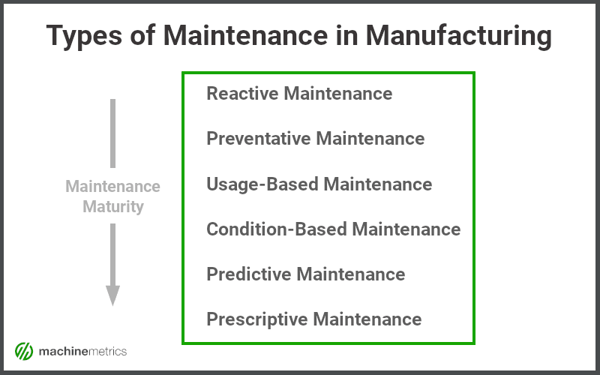
What is Preventive Maintenance?
Preventive maintenance, also known as Preventative maintenance, or simply PM, is a maintenance strategy that involves engaging in maintenance activity with the goal of preventing machine downtimes and failures.
Generally, this strategy relies on a calendar provided by the machine builder, with a recommended cadence for carrying out maintenance activities. However, this can also be based on other variables such as usage.
A step forward from reactive maintenance, preventative maintenance can help ensure equipment uptime, prevent machine failures, and extend asset life.
Despite the benefits, a downside of using a preventive strategy is that it is likely that you may over-spend on unnecessary maintenance activity. After all, the calendar-based recommendations are likely to be conservative estimates from the machine builder.
Furthermore, such a strategy does not take into consideration other variables such as the environment the equipment is in, conditions of the equipment, how well operators manage it, etc.
What is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive Maintenance, or PdM, is a strategy that relies on equipment condition data to inform manufacturers of when maintenance is needed.
PdM could be considered a form of preventive maintenance since it involves anticipating and preventing equipment failures, but is more complex and efficient.
Based on the collection of machine data, manufacturers can establish baselines on one or many conditions. As the equipment is monitored, manufacturers will be notified when a condition reaches a certain threshold that would indicate an impending downtime.
At this point, maintenance would be dispatched to complete the activity.
The efficiency of this maintenance strategy is that maintenance is only completed when it need to be, rather than when it is scheduled to be, thus ensuring equipment is not over-maintained. However, this strategy would also involve collecting equipment data, ideally in real-time, to monitor machine conditions.
A condition monitoring solution such as MachineMetrics can extract and transform equipment data to baseline and monitor equipment conditions in real-time and automatically notify maintenance of impending failures.
Comparing Predictive and Preventative
So, what is the difference between predictive and preventive? Here is a quick summation:
Preventive maintenance is a less advanced maintenance strategy based on predetermined intervals such as time or equipment usage, whereas predictive maintenance is driven by machine conditions, monitored in real-time against established baselines.
Below is a quick breakdown of the differences between predictive and preventive maintenance, as well as a chart that beautifully illustrates how you should think about these two strategies.
| |
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
|
Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
|
| Definition |
A maintenance strategy based on predetermined intervals such as time or usage, with the goal of preventing downtime. |
A maintenance strategy based on real-time equipment conditions, using thresholds to determine when maintenance is needed. |
| Triggers |
Time, Usage |
One or many machine conditions |
| Benefits |
- Generally lower initial costs and easy to implement
- Proactive strategy, a step forward from reactive maintenance
- Limits unplanned downtime
|
- Proactive maintenance strategy, but only done when needed
- More cost effective in the long run
- More effective in reducing downtime than PM
|
| Challenges |
- Could result in over-maintenance
- Does not take into consideration other factors affecting equipment health/performance
- Increases planned downtime
|
- Higher upfront costs (implementation, training)
- Have to connect equipment and have access to data
|
| Learn More |
Article: Industrial IoT and the Move from Preventive to Predictive Maintenance |
Article: How Does Predictive Maintenance Work? |
Taking Your Maintenance Program to the Next Level
How do you take your manufacturing company from a state of reactive maintenance to predictive and prescriptive maintenance? How do you reap the benefits of a modern maintenance strategy while avoiding pitfalls along the way?
Within our "Roadmap to Digital Maintenance Automation" guide, we explore different maintenance strategies and discuss a roadmap to digital maintenance automation.
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)



.gif)






Comments