What Is Machine Maintenance?
Machine maintenance is the process of performing upkeep on machinery to ensure continued working order. It can include maintenance that occurs as part of a regular routine or prior to any sort of break or damage—things like cleaning surfaces, lubricating gears, and checking for wear and tear on parts like belts. It can also involve monitoring equipment for any signs of potential trouble ahead, such as a change in vibrational patterns or an increase in temperature or energy consumption. Machine maintenance also includes the processes that occur after a machine breaks down, such as assessing damage and replacing parts.
Essentially, anything that keeps a machine on the factory floor functional and working as intended can be considered machine maintenance. Machine maintenance services are usually performed by maintenance technicians and are supported by data from the machine control, sensors, and machine interfaces that help assess when maintenance is—or will be—required.
How Do You Maintain Machinery?
There are multiple approaches to machine maintenance, each of which can be used strategically depending on the machinery in question and the predictability of its maintenance needs.
In many scenarios, more mature and complex maintenance strategies yield the most machine uptime and cost savings. Advanced maintenance strategies like predictive and prescriptive maintenance use machine monitoring technology to gather information about factory floor machinery which is then processed and used to generate insights about impending maintenance needs.
Data can be collected via Industrial IoT devices and sensors, as well as from operators at machines. This information can be gathered and analyzed in real-time and used for near-instant insights that can prevent major machine damage as well as boost floor worker safety. This type of data can also be used for longer-scale insights that can guide decisions such as how many spare parts to keep on hand at any given time.
Machine monitoring supports maintenance approaches that can not only predict and prevent machine downtime and damage, but also prescribe solutions on how and when to perform maintenance to fix issues in order to achieve maximum efficiency. This means using parts fully and replacing them as close to the moment of failure (or decline in quality) as is reasonably possible.
For highly predictable machinery, some aspects of maintenance can be managed equally as well with less complex strategies such as usage-based preventive maintenance. A non-manufacturing example of this is changing car engine oil after a set number of miles. In almost all cases, a combination of strategies that leans toward a more data-centric approach will lead to the best results.
Types of Machine Maintenance
If you would like to dive deeper into the different types of maintenance, we have a complete article on the topic, but here is a quick summary of the different machinery maintenance strategies:
- Reactive Maintenance: When it breaks, you fix it.
- Preventive Maintenance: You schedule replacements ahead of time before parts break, usually at a regular interval.
- Usage-Based Maintenance: You replace parts when the machine has been used a certain amount before they break.
- Condition-Based Maintenance: You replace the parts when they seem like they are getting too worn out to continue to function appropriately.
- Predictive Maintenance: You utilize historical data to make predictions about when a part will break and replace the parts based on these predictions, prior to them breaking. This usually, but not always, utilizes artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Prescriptive Maintenance: Advanced data analysis methods are used to do more than predict failure points, but instead provide hypothetical outcomes in order to choose the best action that can be taken prior to failure, safety hazards, and quality issues arise as well as the timing of implementation.
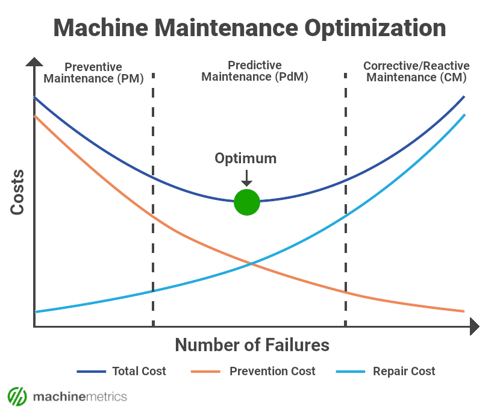 Predictive Machine Maintenance is the “Goldilocks” maintenance solution, in which manufacturers are able to fix problems before they happen, but not overspend on unnecessary maintenance activities.
Predictive Machine Maintenance is the “Goldilocks” maintenance solution, in which manufacturers are able to fix problems before they happen, but not overspend on unnecessary maintenance activities.
How Can You Improve Your Machine Maintenance?
One of the most effective ways to improve machine maintenance for most manufacturers is to focus on data collection and analysis. Data-driven maintenance saves resources and provides benefits in a variety of ways:
- Replacing parts only when necessary, instead of wasting still-usable parts
- Reducing downtime due to unexpected failures
- Reducing the time required by maintenance staff
- Reduced risk of machine and safety incidents caused by ill-maintained machinery
- Reduced storage space required to keep excess stores of replacement parts
- Increases predictability that can guide budgets, schedules, production expectancies, etc.
In order to collect accurate, real-time machine data, manufacturers can use machine monitoring software, such as MachineMetrics, to connect directly to the control of the machine. This machine data is contextualized for a variety of stakeholders to consume across the factory. And depending on the maturity of the manufacturer, the data can be used in increasingly valuable ways.
Plug-and-play Machine Connectivity
For example, manufacturers can simply use machine monitoring to see when machines are down and deploy maintenance to fix the problem as fast as possible. However, more advanced manufacturers will not want to incur the cost of such a large amount of machine downtime.
An alternative to the reactive approach to maintenance is condition-based maintenance. Manufacturers are enabling the information from the machine control and sensors to communicate the health of the equipment and trigger notifications prior to machine failure.
In this way, manufacturers can work towards keeping machines running without spending large amounts of time and money on a calendar-based strategy that over-maintains equipment. Improving a maintenance program will follow along the lines of using more data to drive a more advanced strategy, with each step driving greater machine uptime while reducing costs.

In order to determine which aspects of data-driven maintenance are the best candidates to focus on, consider the following:
- Collecting data allows you to know where you stand. Without being able to measure your maintenance program, you can’t know if you’re improving.
- Having accurate data allows you to identify, and work towards preventing the most notable reasons for failure and necessary machine maintenance.
- Real-Time Machine Data means the team can take action now to prevent or correct issues.
Focus on collecting machine data to develop a better understanding of how equipment is performing. With this key piece in place, it becomes much easier to know if and when maintenance resources should be alerted to handle failures and potential failures.
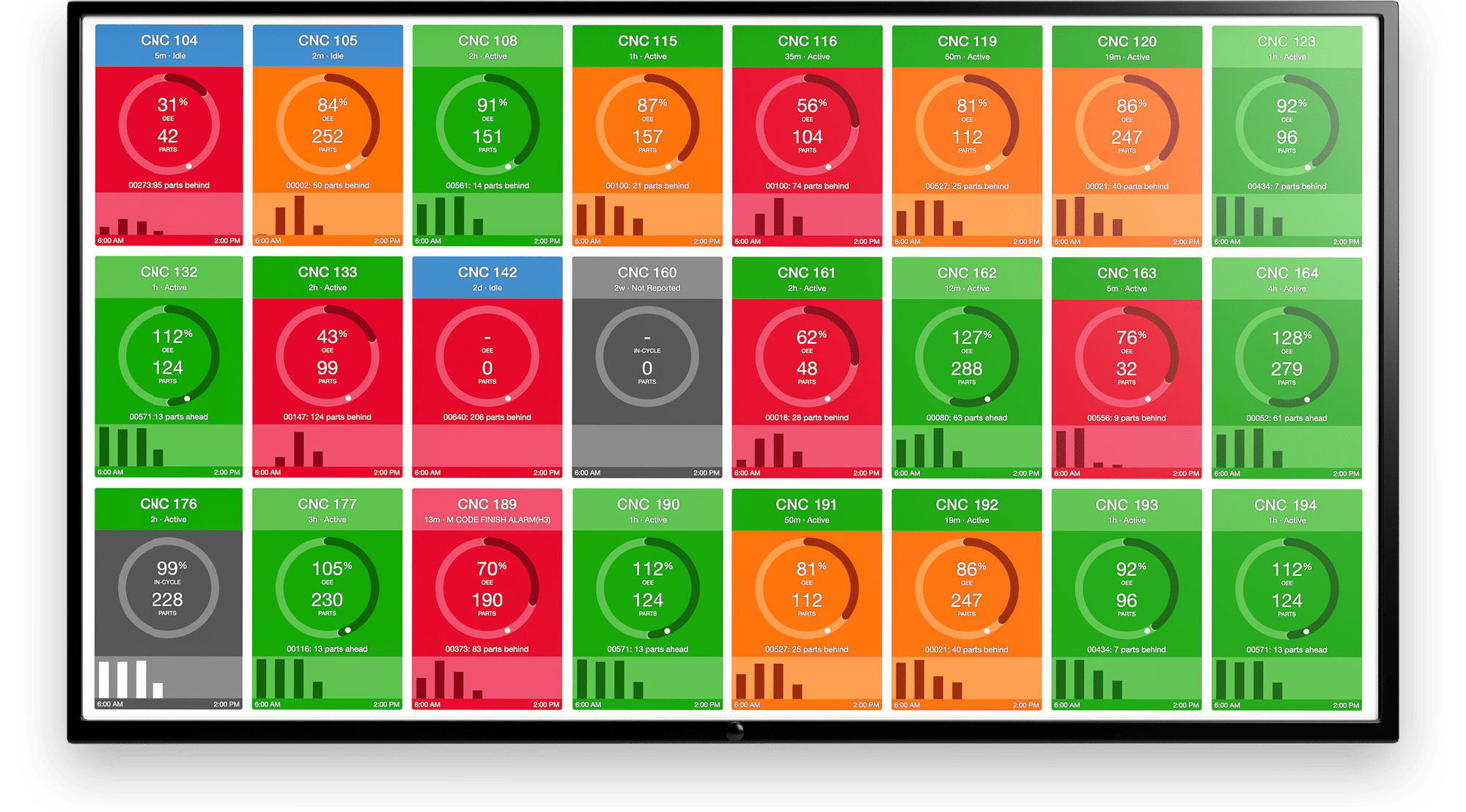
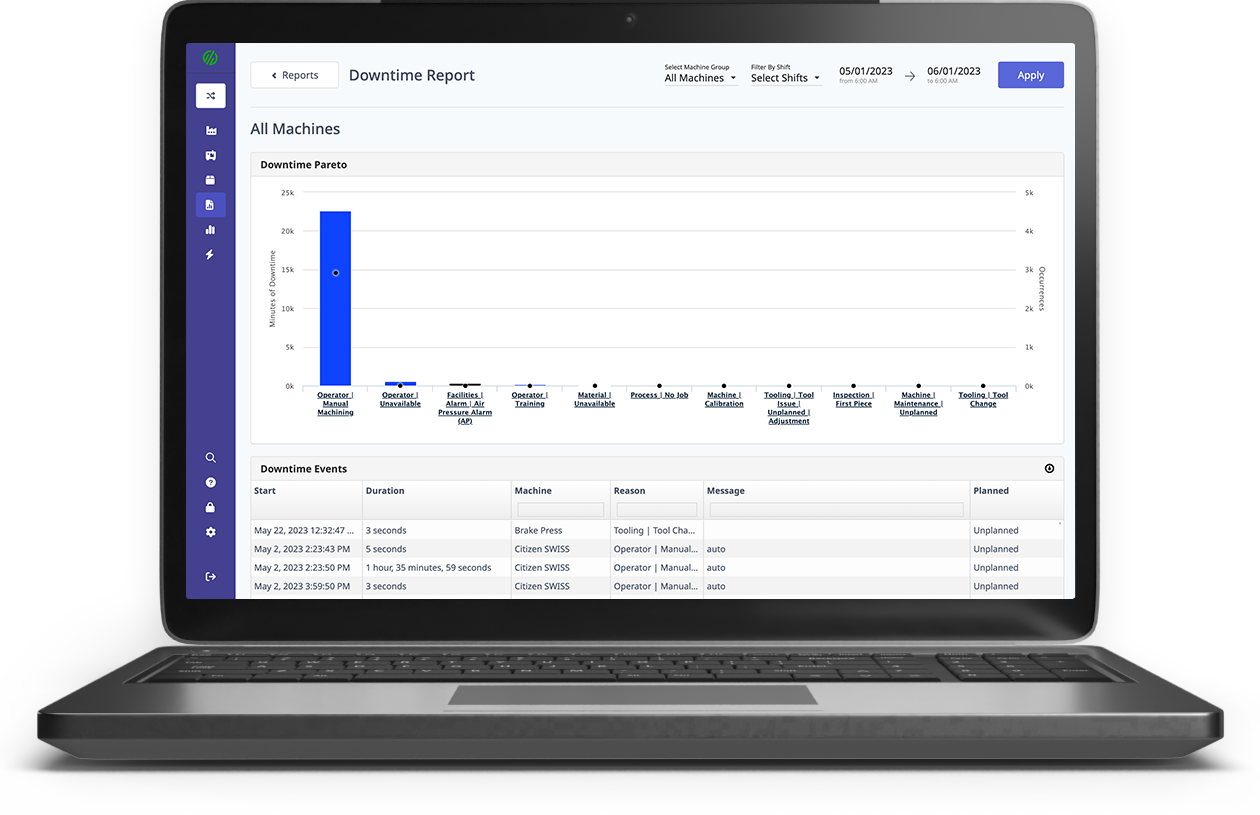
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)



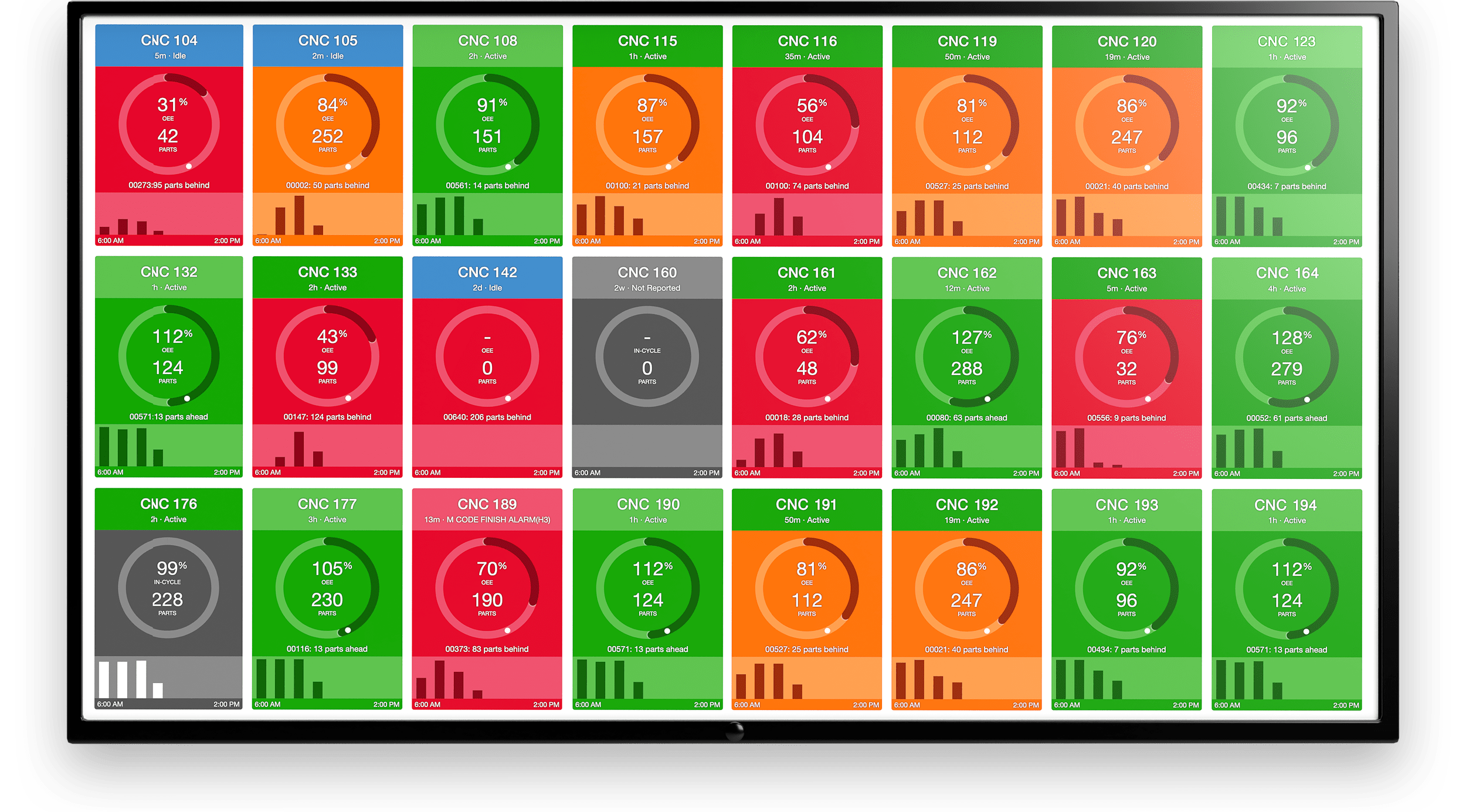


.gif)






Comments