Manufacturing industry process manufacturing software has been around for many decades. As it has evolved, it has revolutionized production processes across different industries. It is used in process, discrete, and mixed-mode production to manage, track, and improve production.
Companies that use manufacturing production software can grow their businesses by enabling greater control of processes and resources to drive optimal output. These manufacturers can better control and manage costs and processes, improve product quality, and ensure timely customer shipments.
What is Manufacturing Production Software?
Manufacturing production software for manages the many functions and processes of end-to-end manufacturing, including material supply and inventory, labor and equipment costs, performance tracking, production planning, and accounting.
Traditionally, production companies managed manufacturing processes manually. This included tracking, change orders, inventory management, equipment condition, and more. These manual steps were often error-prone, inaccurate, open to biased analysis, and usually outdated, immediately creating a lag between understanding needs and the execution of solutions.
Paper-based manufacturing is time-consuming, error prone, and not scalable.
The computer age introduced an ever-increasing and evolving software ecosystem that allowed companies to automate these processes for better accuracy and control. Early systems were usually on-premises and costly, making them attainable to only the largest of enterprises.
As software development evolved, new deployment models, such as software as a service (SaaS), began to level the playing field. This opened the door to modular, customizable, cloud-based, lower-cost process manufacturing software solutions and enabled small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) to utilize the same level of software as larger competitors.
Today, production management software used in manufacturing is flexible and agile and introduces automated functionality to plan, execute, manage, monitor, and adjust production systems and production scheduling, deploy robust quality management, and accurately plan the supply chain. This includes visibility from incoming inventory from the supply chain through lifecycle management, depending on the product.
The Importance of Using Production Software
Production manufacturing software is essential because it provides the automated capability to control costs and optimize processes. In fast-paced production environments, process manufacturing software optimization is critical as it automates the tracking and analysis of production from start to finish.
This means that all aspects of manufacturing can be controlled and executed under one umbrella. Production management solutions can view progress, identify bottlenecks, and act to clear them with access to data and analysis at the spindle, machine, or shop floor level.
Manufacturing software also offers production scheduling that helps manage the workflow within production. It can be linked to scheduling software and other ERP or quality management software platforms. It helps to better control costs and manage the production process. It can ensure that production levels are on track and the right mix and balance of orders are running at the most efficient rate while still meeting customer demands and increasing customer satisfaction.
What Are the Types of Manufacturing Production Software?
Many types of production software for manufacturing are available, and the marketplace for solutions can be quite confusing, given the variety of features available. Many can be used alone or in combination with other software.
The most important component in building a solution ecosystem is ensuring the management systems can access the most accurate, real-time data possible. This ensures processes can be optimized according to facts, not gut instinct or estimates. The source of this real-time production data is the machine assets across the shop floor, and their data can be unlocked with a machine data platform.
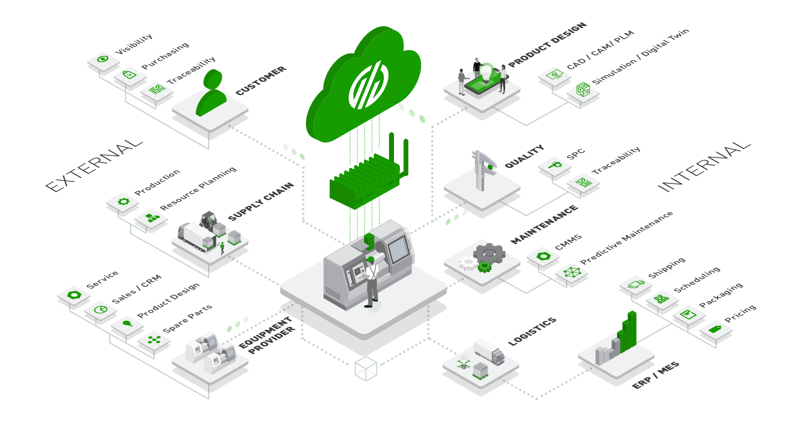
With the machine data component in place, other production software solutions will become far more effective:
Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
MRP is one of the oldest software platforms used by manufacturing businesses. In MRP, productivity is increased on the shop floor by managing the inventory levels required for producing goods. With multi-level BOMs, MRP can explode raw materials down to the component level with the amount needed for each part. It can be further linked to purchase requirements and "on-hand" versus "available" inventory. Production schedules can be produced to optimize the right product and activity on the shop floor.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP is used in manufacturing businesses at the enterprise level. Manufacturing ERP software platforms have the same functionality and purpose as MRP but link these functionalities to human resources, accounting, purchasing, sales, and marketing. The added data layer can make the MRP functionality more dynamic and accurate as it is tied directly to incoming sales and demand data.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
MES is a type of manufacturing solution that signals an attempt to tie raw materials processing through the shop floor all the way to finished goods in real time. Manufacturing execution system software can manage various functions across the operation, including quality control, production, maintenance, labor, and others. The downside of MES is that the data supporting how these functions are managed is based on inaccurate, delayed data, and the overall approach is material and process-centric.
Industrial Data Platforms
The first step in any Industry 4.0 journey is unlocking the machine data from the assets actually engaging in production. With the right solution, data from varying makes and models of equipment is standardized into a common data model and instantly available in pre-built reports for consumption.
This data, coupled with key contextual data from operators, provides the foundation for a digital thread that can be leveraged in a cross-functional, scalable approach, that will not only provide immediate insight into production performance but fuel other management systems with the accurate data they need to manage their corresponding functions.
Top Manufacturing Production Software Benefits
For companies looking to improve their manufacturing practices, there are many benefits to tracking and managing manufacturing production with software. With the right ecosystem of solutions in place, an unlimited number of use cases can be supported. Here are some of the primary benefits:
1. Improved Inventory Management
Inventory purchasing and holding costs can drag a company's cash flow. With automated inventory tracking, manufacturing operations can realize better inventory control to ensure they have what they need when needed.
2. Better Labor and Equipment Utilization
With MRP, shop floor activity can be planned to meet the complexity of the product mix. This means better utilization of labor resources. With machine monitoring solutions, manufacturers can also squeeze greater capacity out of their equipment by identifying and reducing downtime and other forms of waste.
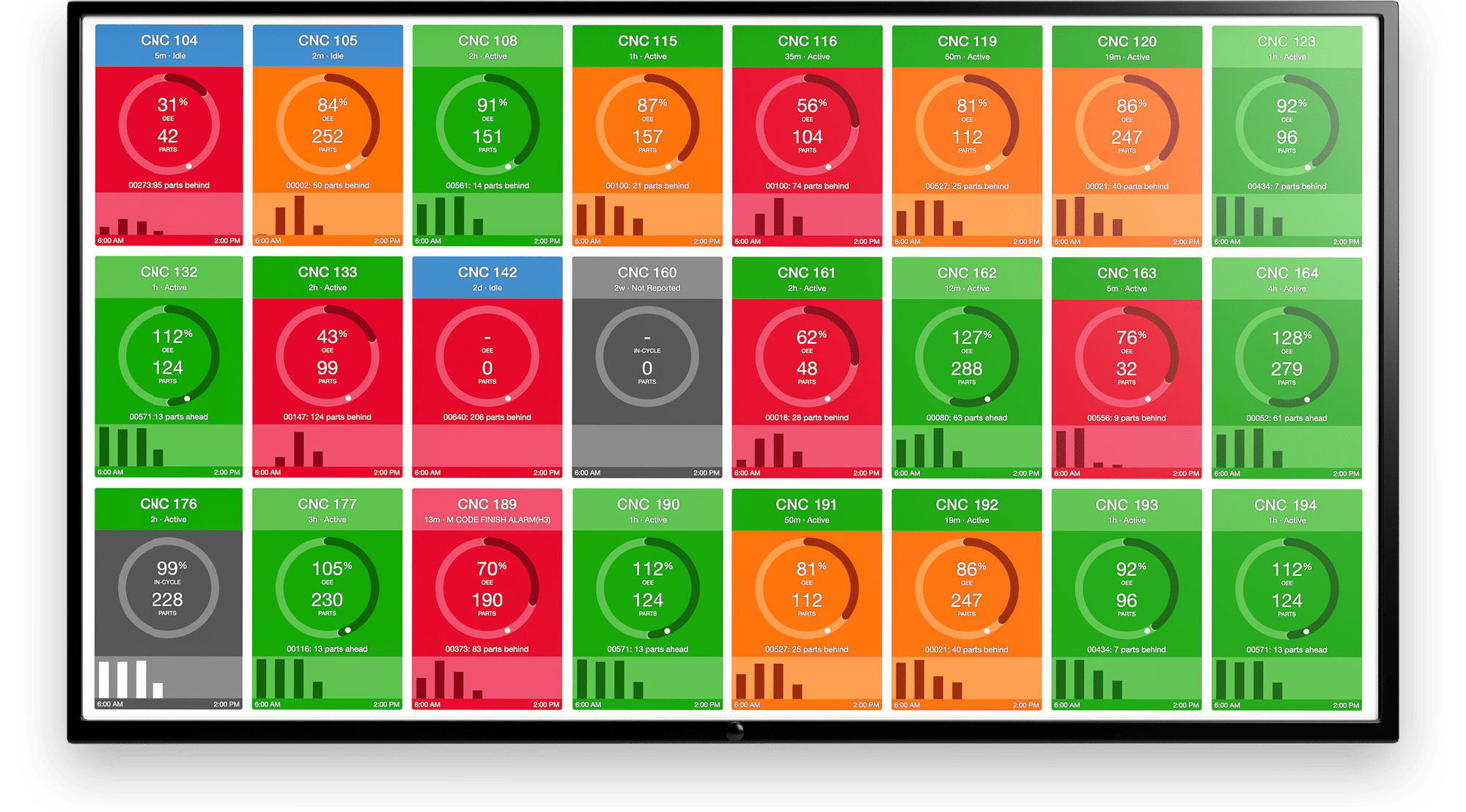
3. Improved Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Companies can optimize processes and unlock capacity with reliable schedules that reflect accurate BOMs and routings. Downtime can be reduced with scheduled maintenance done during changeovers. You can also quickly adjust schedules impacted by a breakdown. This improves OEE and reduces CAPEX spending.
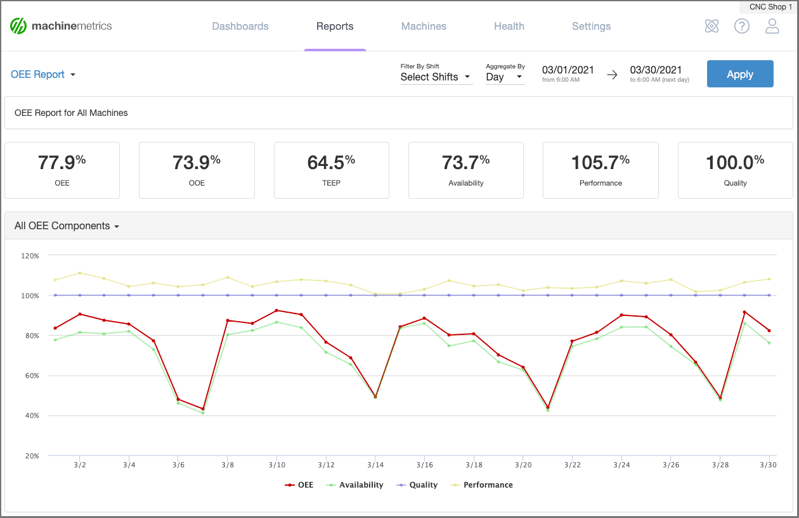 OEE reports from MachineMetrics can provide real-time insight into where you stand against production goals.
OEE reports from MachineMetrics can provide real-time insight into where you stand against production goals.
4. Optimized Purchasing
Because production manufacturing software allows for cost rollups into the BOM, it can be linked to machine speed, product mix data, and other incoming information captured at the machine. From this, economic ordering strategies can be developed to enhance supply chain models with dynamic purchase order management.
5. Enhanced Production Planning
With real-time information, scheduling software can work with production and other management software to enhance production schedules' quality, accuracy, and achievability and improve manufacturing processes.
6. Process Optimization
For manufacturing software platforms that also utilize MES or OPT strategies, processes can be improved by eliminating bottlenecks, increasing OEE, and eliminating non-value processes.
Main Manufacturing Production Software Features
Many of these software systems directly address manufacturing needs. Others, such as ERP and MES, either add additional functionality to the platform or are used with other software, such as an MRP. There are many competing software systems out there. When evaluating the one that fits best, look for key features that are especially relevant to manufacturing businesses and understand that there is no one solution that can solve all problems. Here are some features to consider:
Capacity Requirements Planning
Machine speed, spindle speed, and actual and expected efficiency on a per-product basis are measurable and should be included in your software solution. This allows for accurate forecasts of capacity based on existing orders. More advanced software may also include analytics such as "what-if" scenarios for planning capacity when a change in demand or product mix is detected.
Data Analytics
Robust, real-time data analytics allows production management to optimize processes across the shop floor. Features such as this allow this cloud-based and highly visualized and contextualized data to be used in crafting strategies for improvement. This improvement may apply to training, process optimization, purchasing, scheduling, etc.
Material Availability
Material availability is critical in any manufacturing process software. The platform must reflect on-hand material accurately and include functionality for allocated material against what is on hand so the balance can be used for scheduling and planning. It should also be able to link to open purchase orders to close the loop on the supply chain and increase transparency in the movement of materials.
Scheduling
Production planning in today's high-speed manufacturing environments can be challenging. Having the right balance and control of inventory is only half the battle. Software features should include robust scheduling capability. By using real-time or near real-time data, schedules can be made more dynamic, agile, flexible, and achievable when balancing BOMs, routings, labor, and capacity utilization.
Labor Capacity Planning
Like machine capacity, labor capacity must be a component of any manufacturing process software. Due to complexity, Different products will vary from time to completion within the same factory. Labor capacity must be planned in conjunction with machine capacity to reflect the product mix and the complexity of that mix.
Work Center Planning
Routings are a central factor in any robust software system. These routings will be tied to BOMs so that jobs are only sent to the machines that can perform the work. Work center planning is a step beyond capacity planning, as not all jobs can be mechanically done on all types of machinery. The production floor throughput can be balanced by scheduling work centers.
Quality Management
Quality loss is a significant concern for any manufacturer. Manufacturing process software should include tracking and monitoring quality losses at the machine. But this is just one place where quality management requires embedding within the platform. Industries like aerospace and medical devices require rigid product specifications. Having a system that can include this aspect of quality management is vital for those industries.
How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Software
MachineMetrics allows manufacturing companies to harness machine data's power to enhance performance further. Instead of allowing systems to depend on manual data input, rounded numbers, or estimates, your management systems can rely on real-time, accurate machine data, straight from controlling your assets on the shop floor.
MachineMetrics can work across many different software systems, such as MRP, MES, or ERP. This includes production monitoring and conditions monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization to take advantage of the manufacturing software's functionality and enhance its value.
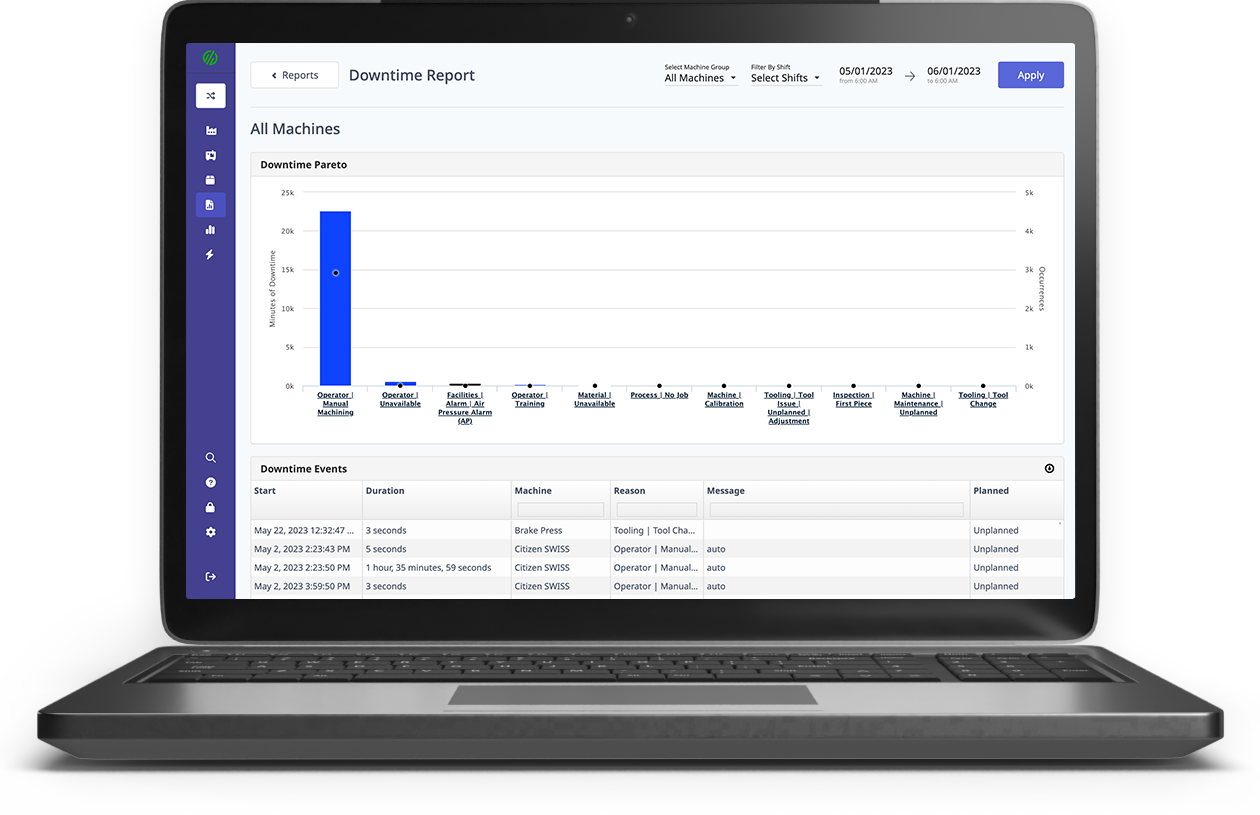
MachineMetrics Production Monitoring can connect to any machine and helps identify bottlenecks so you can optimize your processes. With real-time visibility and machine utilization monitoring, MachineMetrics delivers powerful cloud-based manufacturing analytics software.

.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)





Comments