Key Takeaways:
- The future of manufacturing will be driven by advanced technologies such as IoT, automation, and artificial intelligence.
- Manufacturers must adapt to emerging trends like data-driven decision-making and smart factory adoption to stay competitive.
- As technology evolves, sustainability and collaboration across supply chains will play a key role in shaping the industry’s future.
What Does the Future of Manufacturing Hold in Store?
As buzzwords go, the Internet of Things (IoT) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) have been prominent features in manufacturing shop floors throughout the last decade, and this isn’t going to change anytime soon. According to Bsquare’s annual survey, 86% of manufacturing enterprises have adopted different forms of IoT to enhance shop floor operations. This makes it only fair to acknowledge the growing influence of IoT, and brings to question how it will continue to be applied in the future.
Since the responsibility of implementing IoT solutions falls on the capable shoulders of CTOs, project managers, and engineers across the globe, here are seven things you need to know about its future.
1. Application is an Individual Thing
Although thousands of vendors offering diverse IoT services and solutions exist, substantial differences in its application still exist across manufacturing enterprises. These differences exist due to the mode of application enterprises choose. Thus highlighting the importance of understanding the different manufacturing variables and data produced within specific shop floors.
This means as data capture from even the deepest parts of manufacturing facilities becomes easier due to advancement in edge hardware and software, the future of IoT will be defined by individual enterprises fine-tuning its application.
2. Hardware Innovations Will Increase Adoption Rate
As with most technical fields, software development takes the shine from other interrelated aspects of a technological movement. This is also the case with IoT and IIoT. Although overlooking hardware development may work for certain industries, manufacturing is definitely not one of them. The fumes, liquids, environmental stress, and topology in manufacturing shop floors means IoT hardware must be durable and come with many IP codes to function properly.
Thus, the future of IoT in manufacturing is highly dependent on the innovations that hardware vendors integrate into the development of IIoT devices. IoT hardware is expected to become the proverbial ‘shovels’ sold during the ongoing IoT gold rush. A Mckinsey research expects IoT to create a $200 billion market for hardware manufacturers within the next five years as the need for more versatile devices increases.
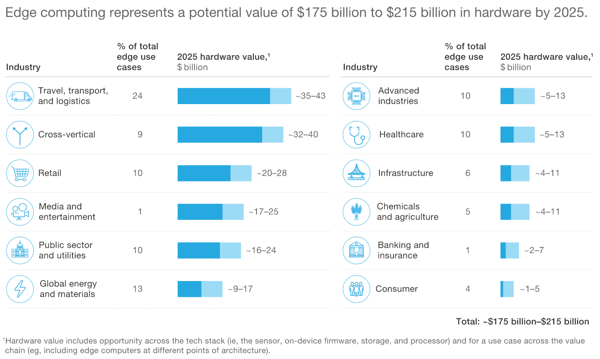 IoT hardware will continued to experience tremendous growth. [Source]
IoT hardware will continued to experience tremendous growth. [Source]
3. Process Optimization through Interrelated Technologies
No technological solution exists in a vacuum. The introduction of IIoT in manufacturing shop floors has created the need for more visibility into causation factors and data transfer within facilities to optimize manufacturing processes. Although IoT devices capture data, proper analytics is required to extract applicable business insights from the captured data. Thus, the next phase of IoT implementation will rely on interrelated technologies such as the digital twin and simulation platforms to deliver process optimization.
It is due to this that IIoT platforms offering enhanced data analytics and business insight services will play important roles in enhancing the integration of IoT in shop floors. This means decision-makers must understand how other interrelated technologies provide better business cases for the adoption of IoT.
4. Predictive Maintenance
In the early days, every IoT applications list came with predictive maintenance as one of the future aspects of IoT implementation and this still remains the case. But there is a twist. The future of predictive maintenance will rely on data accessibility and sharing in new ways. The ability to access outsourced data from hundreds of similar equipment means manufacturers no longer have to base predictive maintenance initiatives solely on the data their assets produce.
Thus, manufacturers can purchase new equipment or set up new facilities with an active predictive maintenance initiative or policy already in place. As you can probably imagine, the benefits include equipment lifespan optimization, reduced expenditure, and spare part inventory optimization.
5. Enhanced Advanced Planning and Scheduling Procedures
Traditionally, advanced planning and scheduling initiatives rely on discrete event simulations to develop manufacturing cycle plans. Thus, even when ERPs or MES vendors tout their wares as providing end-to-end visibility for supply chains, production activity controls (PAC), and real-time scheduling this has not been the case. This is due to the time lags with receiving data from varying sources that affect the ability to deliver end-to-end visibility.
The increased application of IoT and the rise of low latency communication protocols is set to eliminate the visibility gaps in ERP environments. Advancements in digital twin technology coupled with the connected data streams IoT produces is expected to deliver accurate real-time planning and scheduling processes in the future.
6. Enhanced Cybersecurity in Manufacturing Facilities
The cybersecurity threats manufacturing facilities face has continued to increase annually according to The 2019 Manufacturing and Distribution Report. With more than half of manufacturing enterprises falling victim to data breaches, the need for a more-effective threat remediation process is needed. With the integration of IoT, these fears are also increased as more data-producing sources are added to shop floors. But with the introduction of edge computing hardware in association with IoT devices, the security challenges manufacturers face will be reduced as data capture and analytics becomes decentralized.
7. Reduced Manufacturing Costs
The total cost of manufacturing products takes into consideration concepts like labor costs, materials costs, overhead costs, and waste. With predictive maintenance, real-time advanced planning, process optimization, and innovative hardware, manufacturers will experience a reduction in downtime, an inventory waste reduction, and optimal use of capital and human resources. The end result of these IoT application processes is reduced manufacturing costs and enhanced productivity levels.
The Next Steps
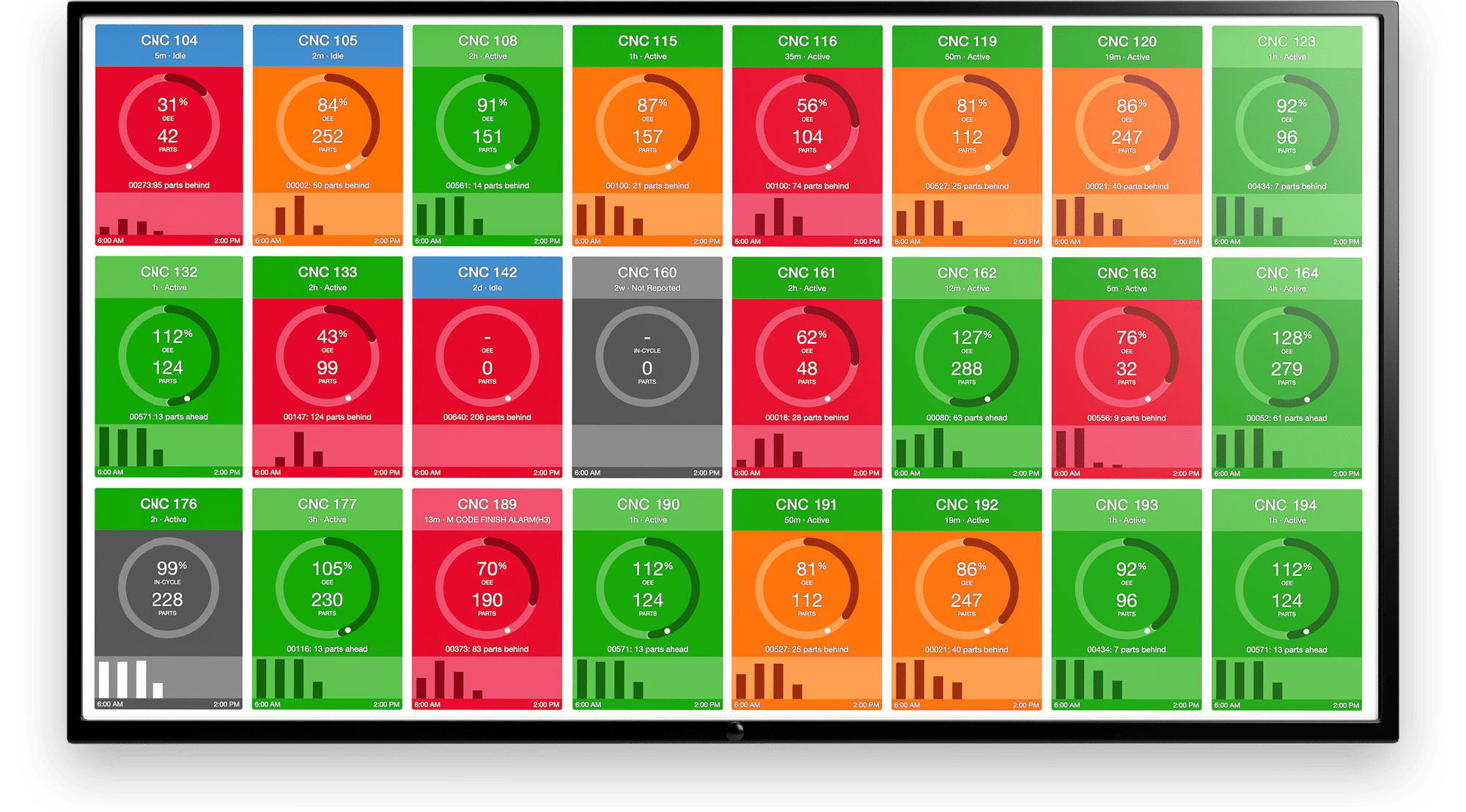
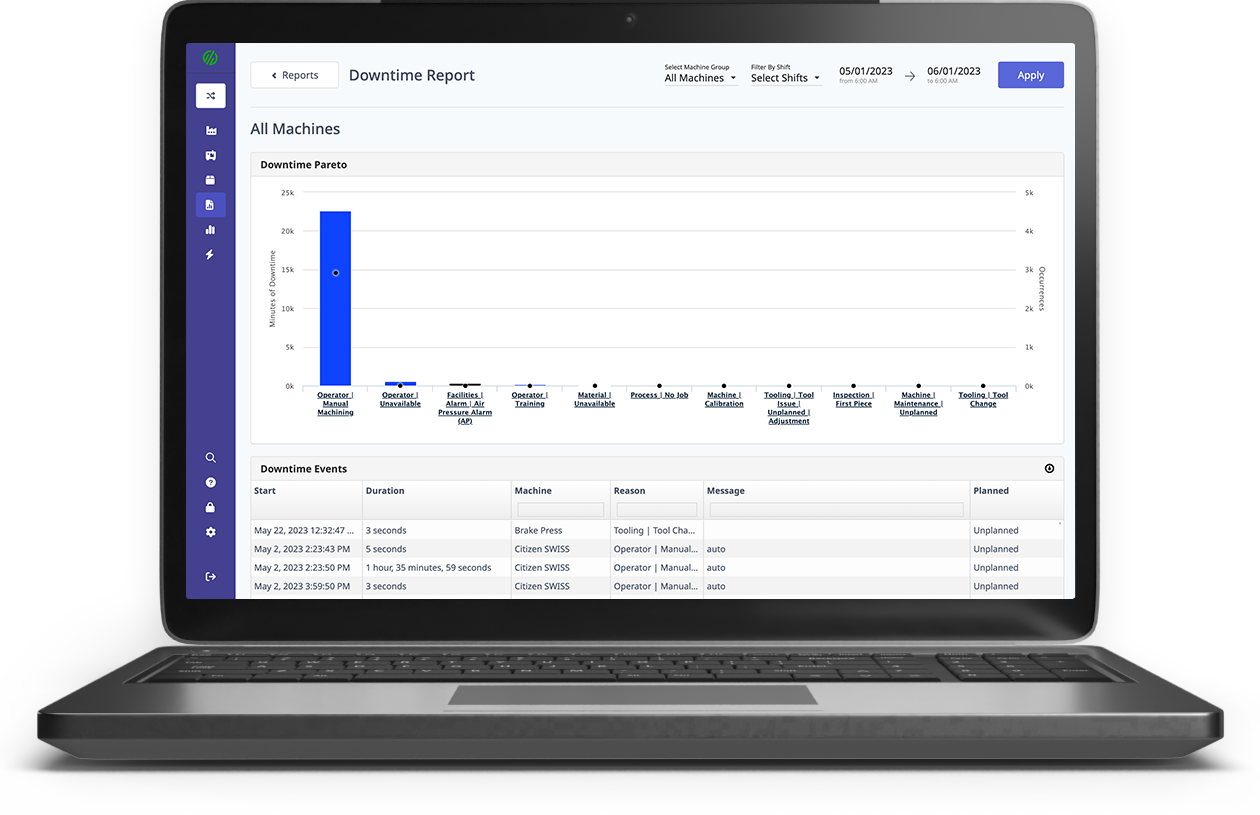
Manufacturers interested in adopting IoT or looking to get the best out of existing IoT structures must understand the future to develop proper implementation plans. CTOs in brownfield manufacturers can look to the hardware and software IoT offerings MachineMetrics provide while drawing up an implementation plan. On the other hand, greenfield facilities can take advantage of MachineMetrics data repository to better understand the data your installed shop floor IoT assets provide. Thus, providing your shop floor with the knowledge needed to apply IoT to enhance specific manufacturing operations.
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)

.gif)






Comments