Whether you are tracking overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), machine utilization, or simply the number of finished parts, manufacturing success comes down to one simple, general goal: production efficiency.
Production efficiency is the standard that manufacturing operations have used to prove how well they’re doing and identify which procedures need to be improved, where bottlenecks exist, what capacity is available, and where to invest time and resources.
It’s a concept easily explained by managers and understood by production workers as a gauge of shop floor performance. Though, it may be defined in many ways depending on the operation in question.
But what is production efficiency, and how are digital solutions driving the next level of efficiency and growth?
What is Production Efficiency?
Efficiency in production is the process of making the largest volume of production using the least available resources. These resources include raw materials, labor, overhead costs, planning, inventory, and more. Efficiency in production means that to produce additional units of any one product in a factory, another product’s total production unit count would need to be reduced.
Companies have long chased production efficiencies because it was seen as a comprehensive performance indicator. The assumption was that high efficiency meant full labor utilization, optimized material consumption, and optimized planning and logistics.
How is Production Efficiency Calculated?
The formula for calculating production efficiency is straightforward. It’s defined as a percentage of the actual output rate divided by the standard output rate:
Production Efficiency = Actual Output / Standard Output
Standard output may be based on industry standards, calculating ideal cycle times, or by using actual machine type, speed, etc. It may also take history and different OEM equipment into account to set a benchmark or “standard”. Actual output is a measurement of total output divided by total input.
What are the Benefits to Efficient Production?
There are many benefits of high production efficiency. These include:
- Higher Profit: If a company is producing efficiently, then profits increase and costs decrease.
- Greater Customer Satisfaction: In an age of more sophisticated consumer knowledge, missed deliveries and shortages are seen as a lack of efficient processes. Higher efficiency means a better ability to provide consistent delivery and meet customer expectations.
- Better ROI on Capex Equipment: If production efficiency is high, managers and executives expect a greater return on investment (ROI) for expensive equipment. It allows them to understand capacity and better plan for future equipment needs.
The Downsides of Focusing Only on Production Efficiency
Production efficiency is historically a helpful metric in gauging factory performance. But it’s one of many metrics that reveal a more comprehensive picture of performance.
There are downsides to focusing too highly on production efficiency while foregoing many of the other elements of a successful operation.
- Quality: Companies pushing efficiency often haven’t made an effort to undergo process improvement. By driving managers and operators to achieve efficiency, quality may suffer. The units scrapped due to fallout drive up the cost of waste and impact inventory, purchasing, and profitability. The production floor may be perceived as efficient, but quality and waste may be out of control.

- Maintenance: In operations where efficiency is the primary metric, equipment may be poorly maintained. Driving faster changeovers without proper cleaning, making “band-aid” repairs, and skipping routine maintenance to drive efficiency will eventually result in extended downtimes and higher maintenance costs.
- Lower Employee Satisfaction: Operators often know where problems are. And they also know the goal of their efforts, whether formally or informally stated. Focusing exclusively on production efficiency means they may be tempted to cut corners on cleaning, minor repairs, and proper documentation.
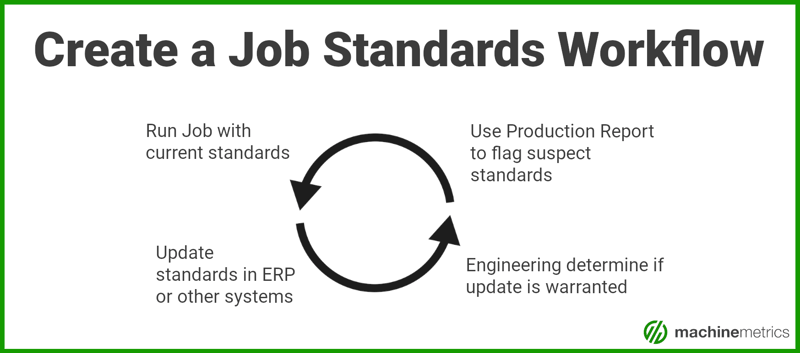
Making the Best of Production Efficiency
There are ways to improve production efficiency through discipline and documentation, and these steps will help reduce the downsides listed above:
- Audit Your Processes: By conducting an honest assessment of processes, many areas for improvement will surface. These include task redundancy, machine layout, operator practices, record keeping, and other variables. Once audited, improvement plans can be implemented to ensure the changes remain in place.
- Standardize Work: As improvements are made, well-written and thoroughly documented steps will help operators and support staff continue the adjusted process by using standard operating procedures. The procedures should represent the most efficient way to perform each task or operation.
- Improve Employee Training: With improved processes and access to standardized work, staff members should be trained to do things the same way. Employee training should be structured according to standard work procedures.
Collecting Accurate Insights with Machine Connectivity
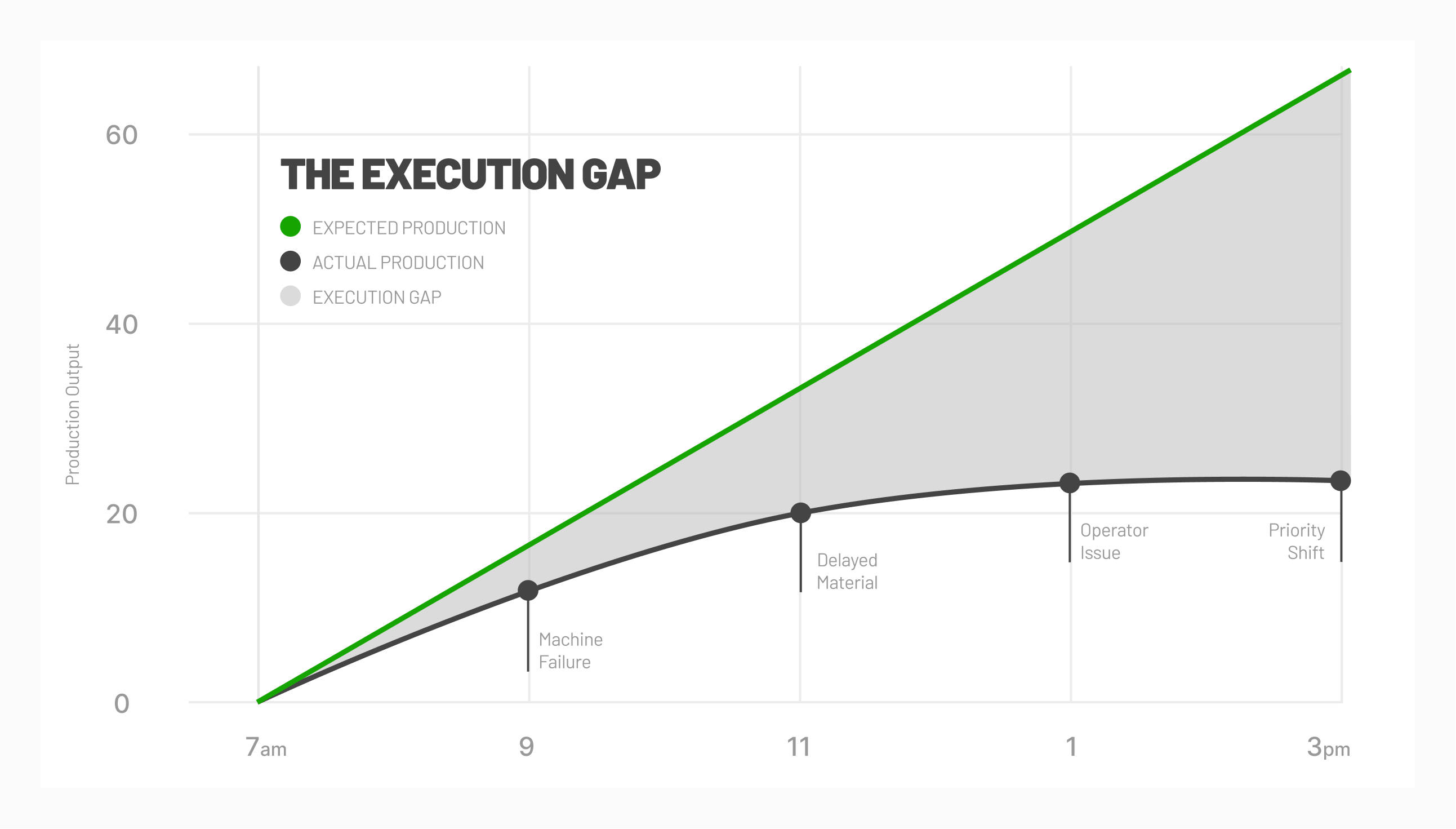
Perhaps the most significant downside to narrowly focusing on production efficiency is its potential effect on operational efficiency. A manufacturing environment is a complex system, and it’s possible that operational efficiency may suffer by focusing exclusively on production efficiency.
One of the major challenges in improving the performance of the shop floor is a lack of production visibility. Many operations continue to rely on inaccurate, delayed data sources. These systems force operators to manually enter data into systems where managers then have to compile and analyze the information in an attempt to understand performance.
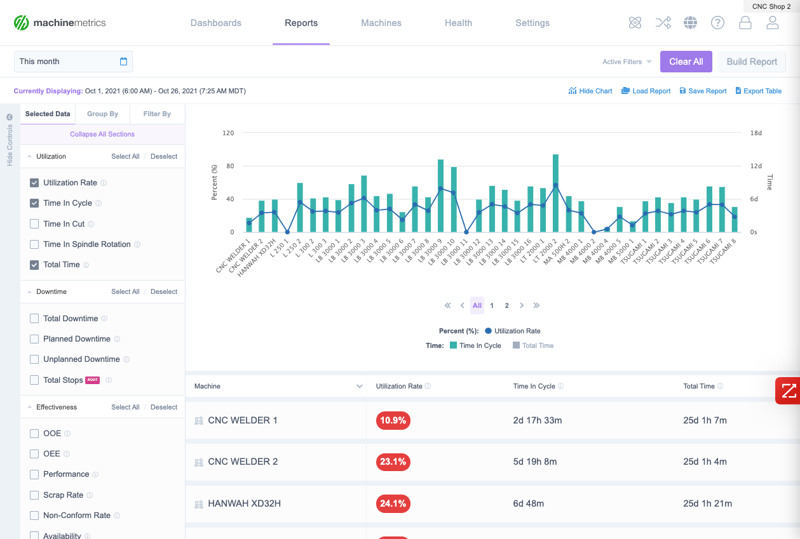
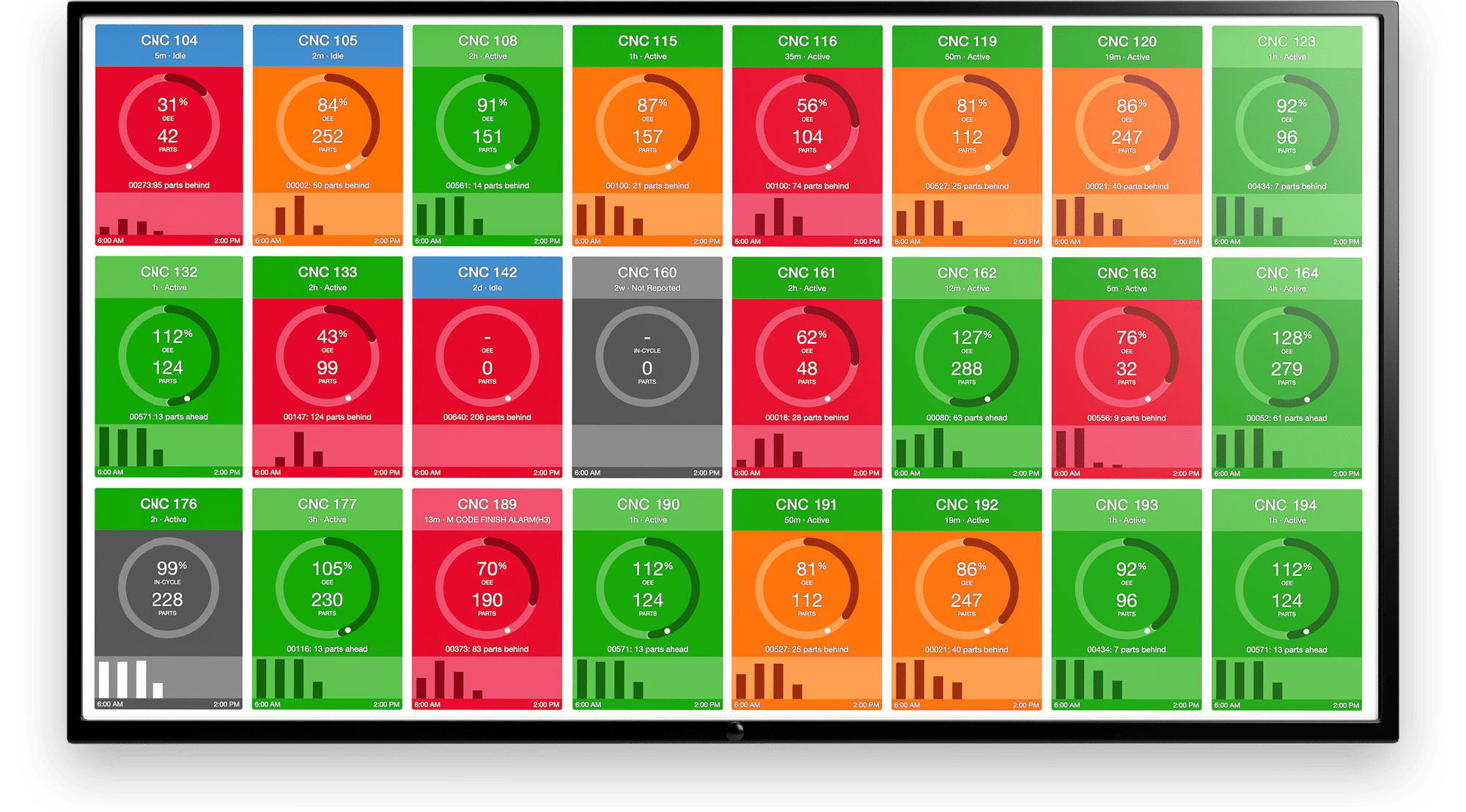
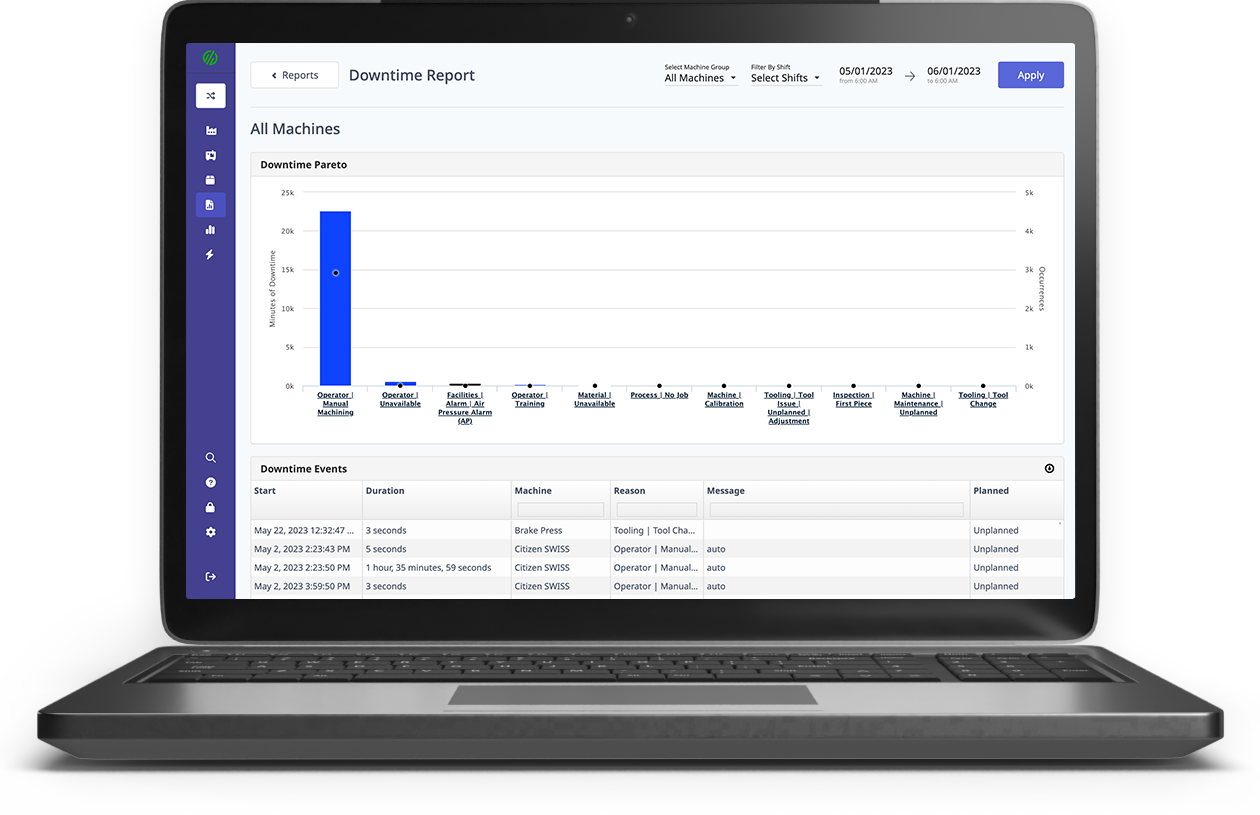
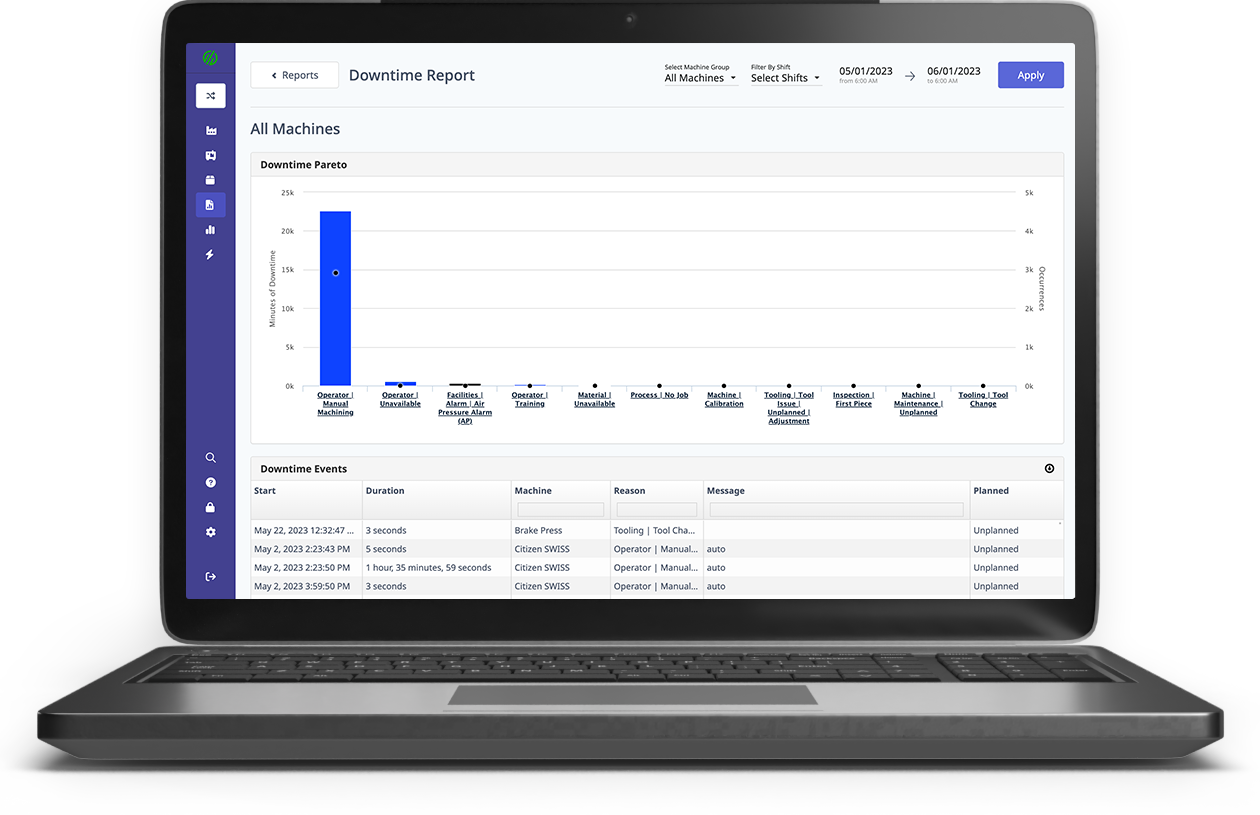
Connected factory environments rely on real-time data collection from equipment to ensure shop floor visibility with accurate, real-time data including part counts, cycle times, downtime, and OEE.
With MachineMetrics, visualization and data collection are automated, real-time, and accurate. Operators not only know their production and performance in real time, but they can also identify exactly where and when they need to intervene.
This gives both operators and managers the insights they need to take action, whether that be identifying when a downtime event occurs with a notification, spotting a process bottleneck, or highlighting existing capacity.
Want to see how it works? Check out a tour of the product:
Want to See the Platform in Action?
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)




.gif)






Comments