What Is Industry 4.0?
The concept of Industry 4.0 is reaching—it covers technologies like industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the cloud, edge computing, and digital twins as well as other defining concepts such as machine-to-machine communication (M2M) and cyber-physical systems (CPS).
The foundation of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is automation. All of the systems that collect and communicate data are there to serve the purpose of making industrial and manufacturing practices more efficient and autonomous.
Technology in IR4 serves to connect previously discrete systems through hardware and software, provide information transparency, augment the human decision-making process, and to decentralize decisions within technological systems so that humans need to interfere less frequently.
Interested in diving deeper on Industry 4.0 technology and benefits? Read our complete guide.
What Does Industry 4.0 Mean for Lean Manufacturing?
In lean manufacturing, organizations prioritize minimizing waste while maximizing productivity. The lean manufacturing production method is a philosophy that works seamlessly with the innovations of Industry 4.0 which serve to support efficiency initiatives at every stage of the manufacturing process. Industry 4.0 helps lean manufacturers save time, money, energy, and material resources, and human resources, especially when multiple IR4 technologies are deployed simultaneously.
As Industry 4.0 continues to mature, and as we enter the Fifth Industrial Revolution (IR5), manufacturers can expect to see data and IR4 tech as a competitive advantage over less technologically mature organizations. The optimizations that they are able to achieve will become—and in most cases, have already become—impossible to replicate with human knowledge, intuition, and willpower. The simple reason for this is that humans cannot collect and analyze data with enough accuracy or at speeds fast enough to derive the sorts of complex analytics and real-time insights that are able to be achieved through IIoT, machine learning, and other Industry 4.0 technology.
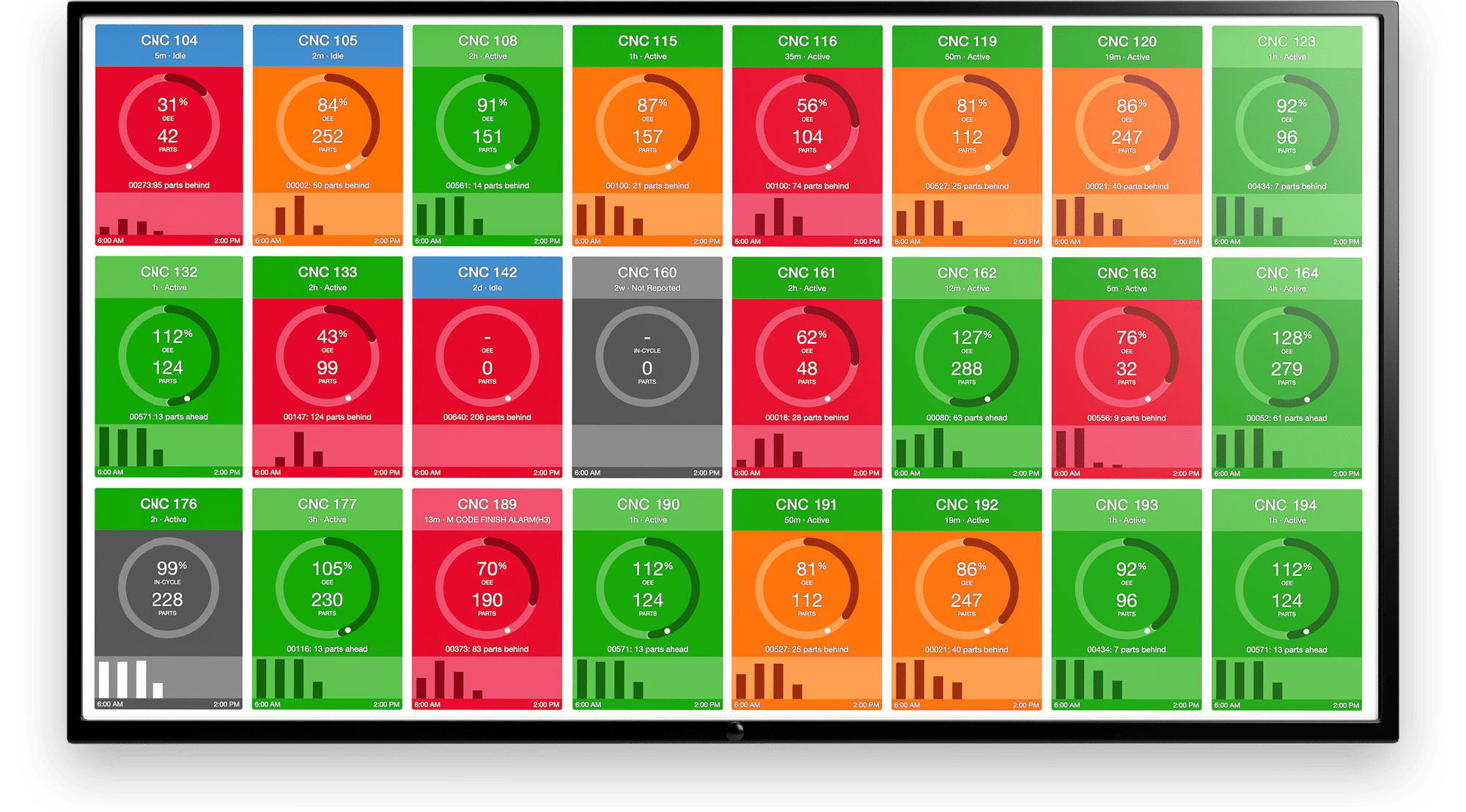
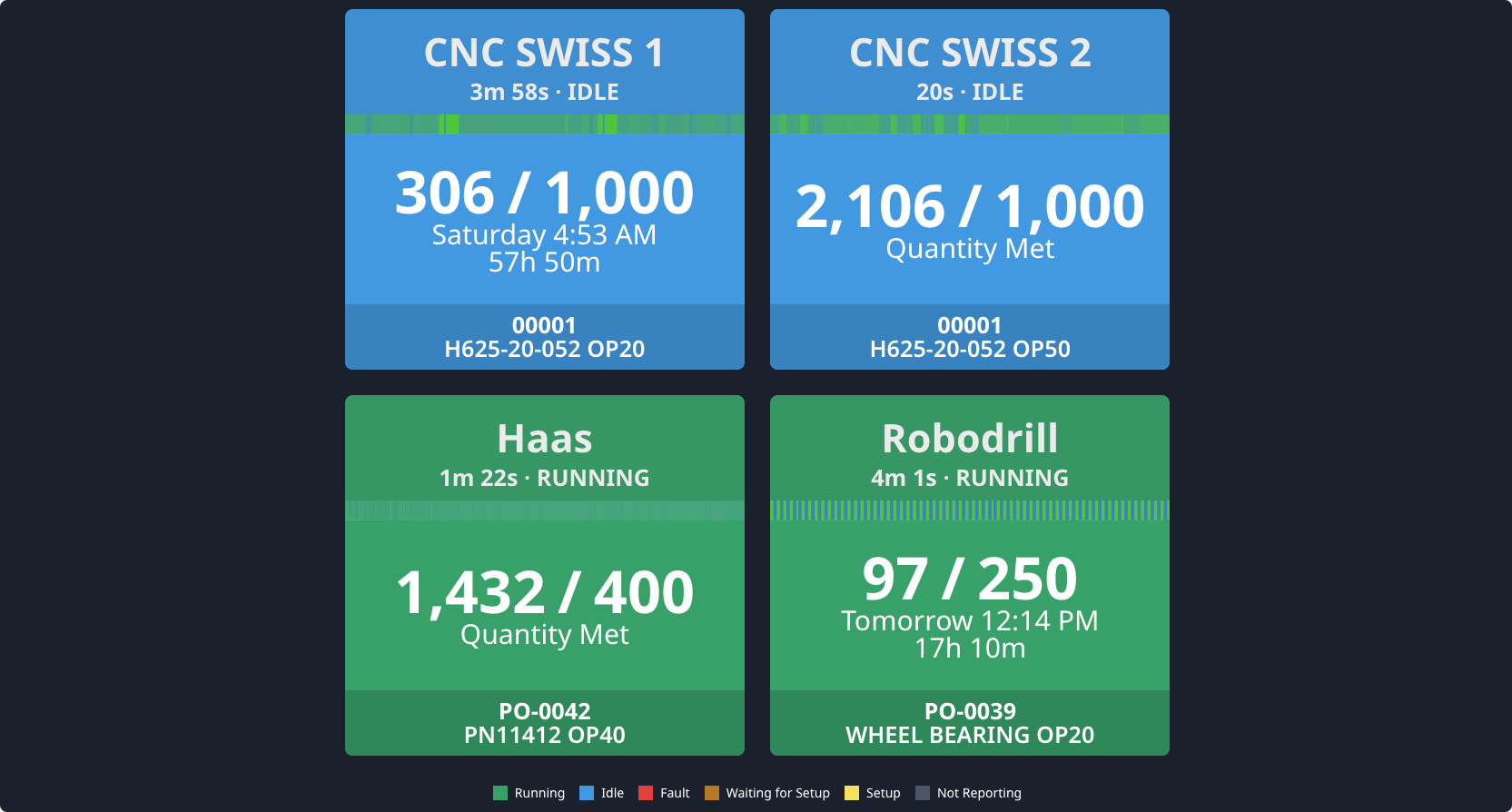
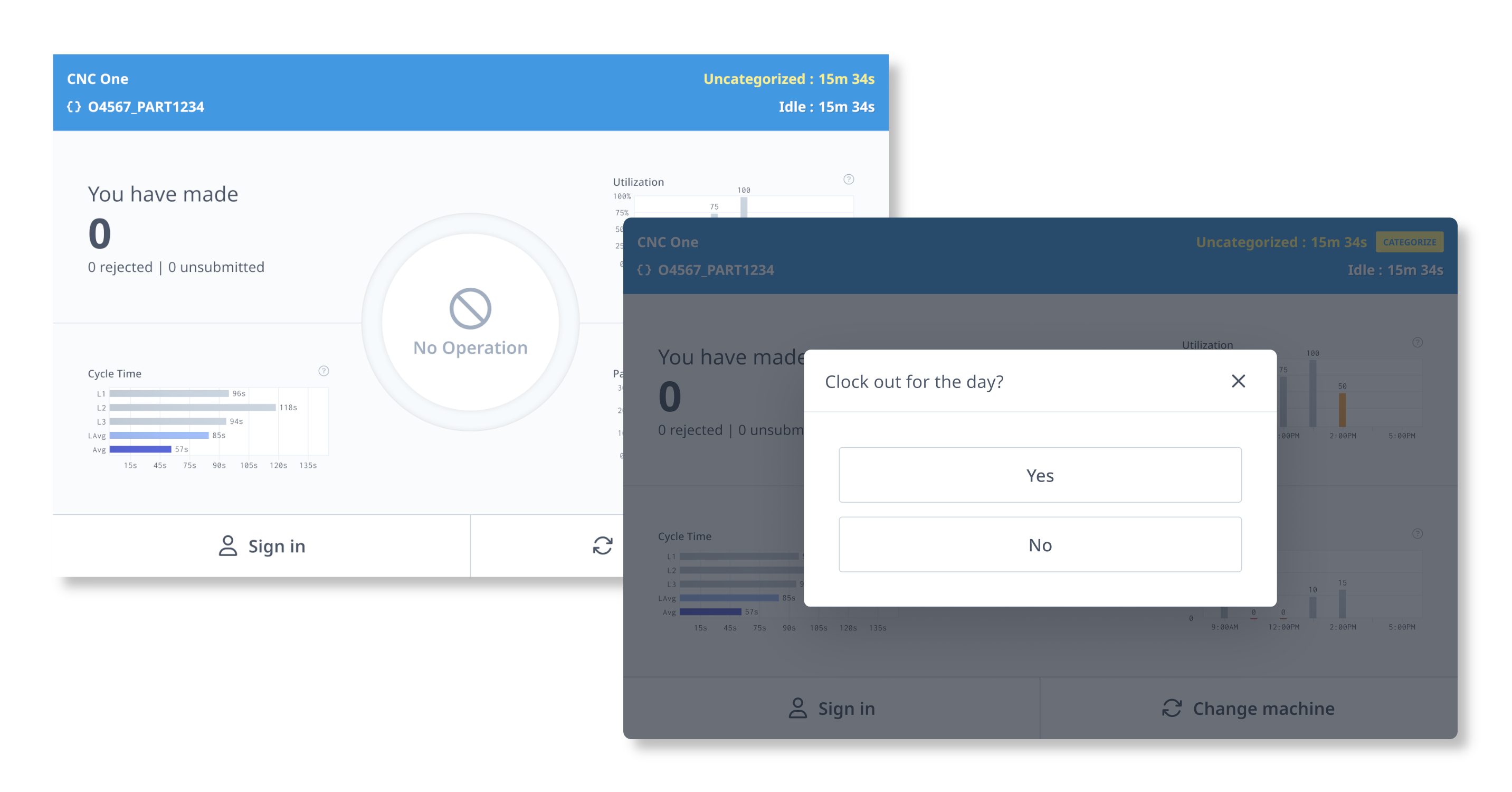
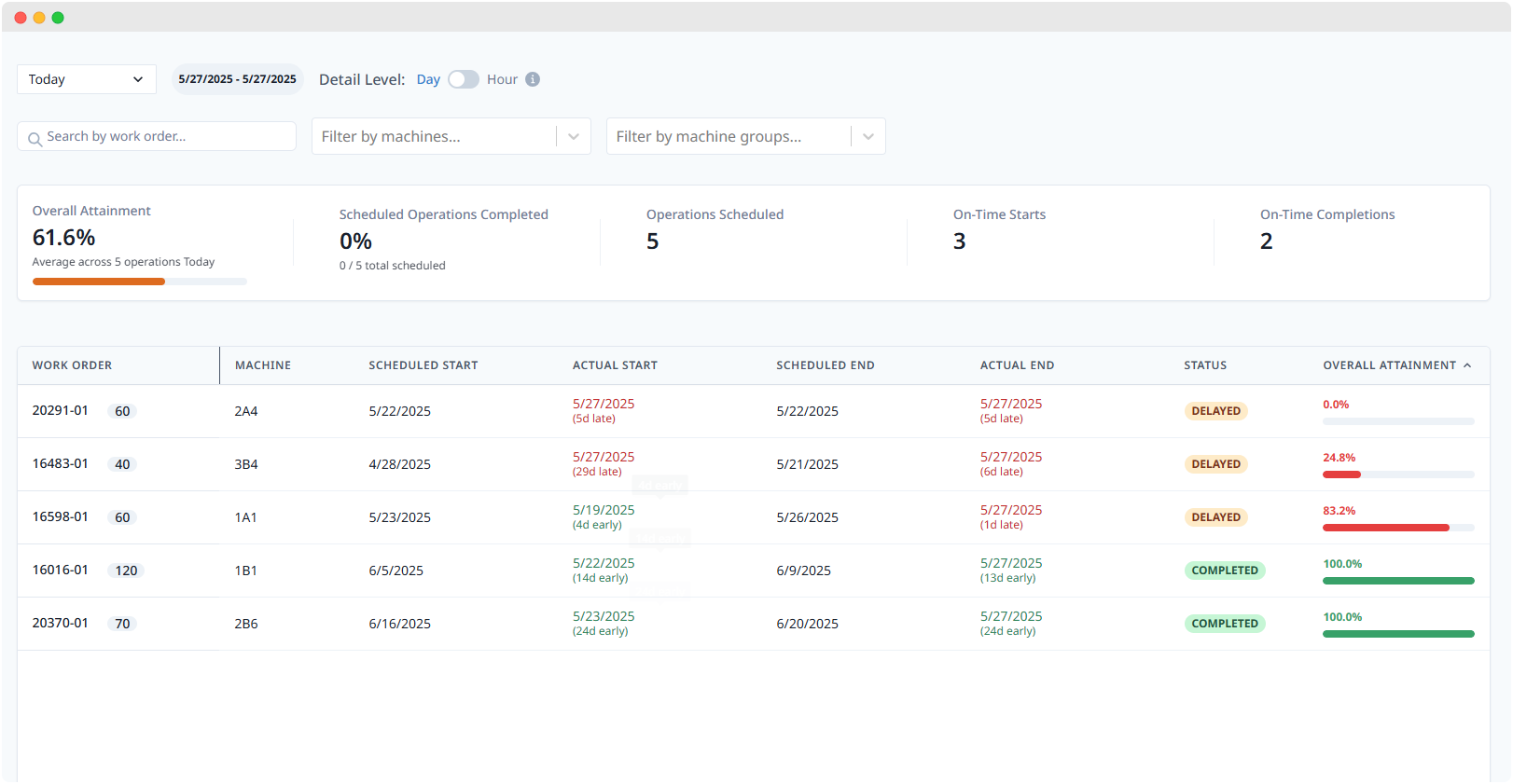
Manufacturers who use Industry 4.0 tech are able to reduce downtime through predictive and prescriptive maintenance using sensors and other IIoT devices, maximize machine utilization, quickly pivot and innovate in response to market fluctuations, identify and mitigate bottlenecks, make real-time choices such as automatically stopping a machine in the case of a safety issue using Edge computing, increase shop floor visibility, optimize warehouse space and other sources of overhead, and make more informed decisions across the board using visualized data. The list of use cases is infinite if manufacturers are able to build the right infrastructure that can support the collection and transformation of data.
A Complete Guide to Lean for Manufacturers
How Lean Manufacturers Use Industry 4.0 Technology to Boost Efficiency
Smart factories are among the biggest trend in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and are a prime example of the digitization of vertical and horizontal value chains, serving as a showcase for nearly all of the defining technologies of the era. Some of the Industry 4.0 technology that lean manufacturers use in smart factories include the below solutions, but for a comprehensive review, explore our full guide:
Cyber-physical systems and “Digital Twins”
These are digital representations of physical systems such as the factory floor and all of the machinery on it. The CPS connects and monitors the entire factory floor as a system so that it can be monitored and data can be used to guide automated decisions. In these cyber-physical systems, machines communicate with one another as well as with humans.
Smart Sensors
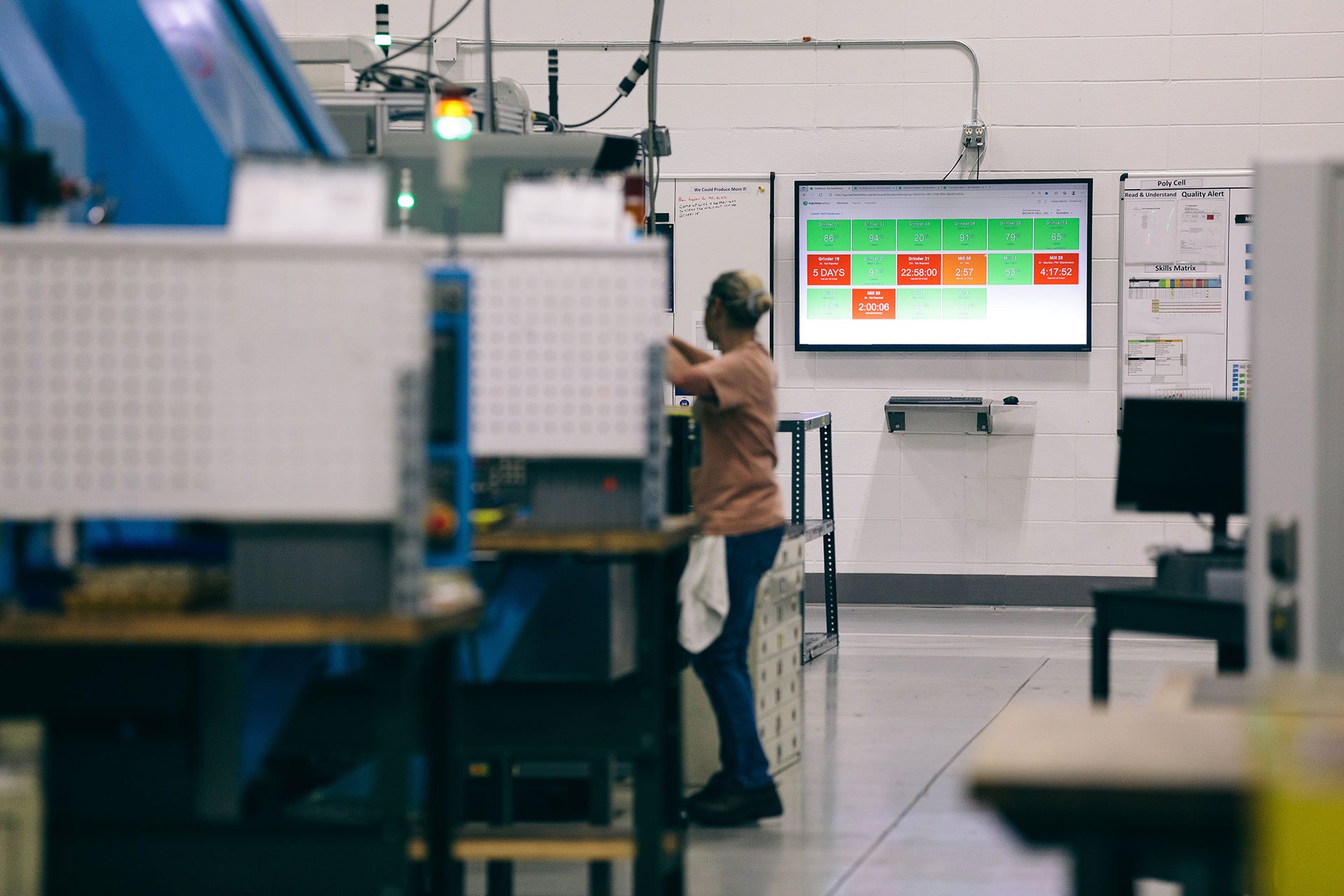
Smart sensors collect data around the shop floor including quality data, part counts, machine utilization, and other key data and metrics. Once this raw data is contextualized, it can be used to guide decision-making across a variety of use cases, and allow manufacturers to pursue advanced strategies such as predictive maintenance.
Edge Computing
Edge computing uses distributed computing resources that are—unlike the cloud—close to the spot where data is being collected. Being able to analyze data in a decentralized way at the factory itself means faster times to insights, ideally in as near to real-time as possible. Speeds from edge computing are fast enough to stop machines immediately if a safety hazard is sensed, and speeds are largely indiscernible from real-time to humans. This is often also used for predictive and prescriptive maintenance to help prevent equipment failures and downtimes.
Predictive and Prescriptive Maintenance
These mature maintenance strategies rely on data collected from sensors and machine interface connectors that is then analyzed in order to develop maintenance plans that fully utilize resources. That is to say that parts are not replaced when they still have notable life in them as often occurs with preventive, usage-based maintenance. It also means parts are replaced before they lose enough effectiveness to reduce quality to an unacceptable level or to risk long-term or costly damage to machinery. With prescriptive maintenance, insights also include possible solutions to issues when optimizing for a particular KPI (or set of KPIs) such as waste reduction or speed.
The Next Generation of Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 is unleashing a variety of technology that is spurring a leaner manufacturing industry. The core of these solutions involves extracting data from operations and using it to drive better, faster decision-making across the business, whether you are in charge of maintenance, quality, production, or the entire plant. Starting with the basics and focusing on the heart of the operation (the machines and people on the shop floor) will help build the foundation for a smarter, connected lean operation.
Want to See the Platform in Action?
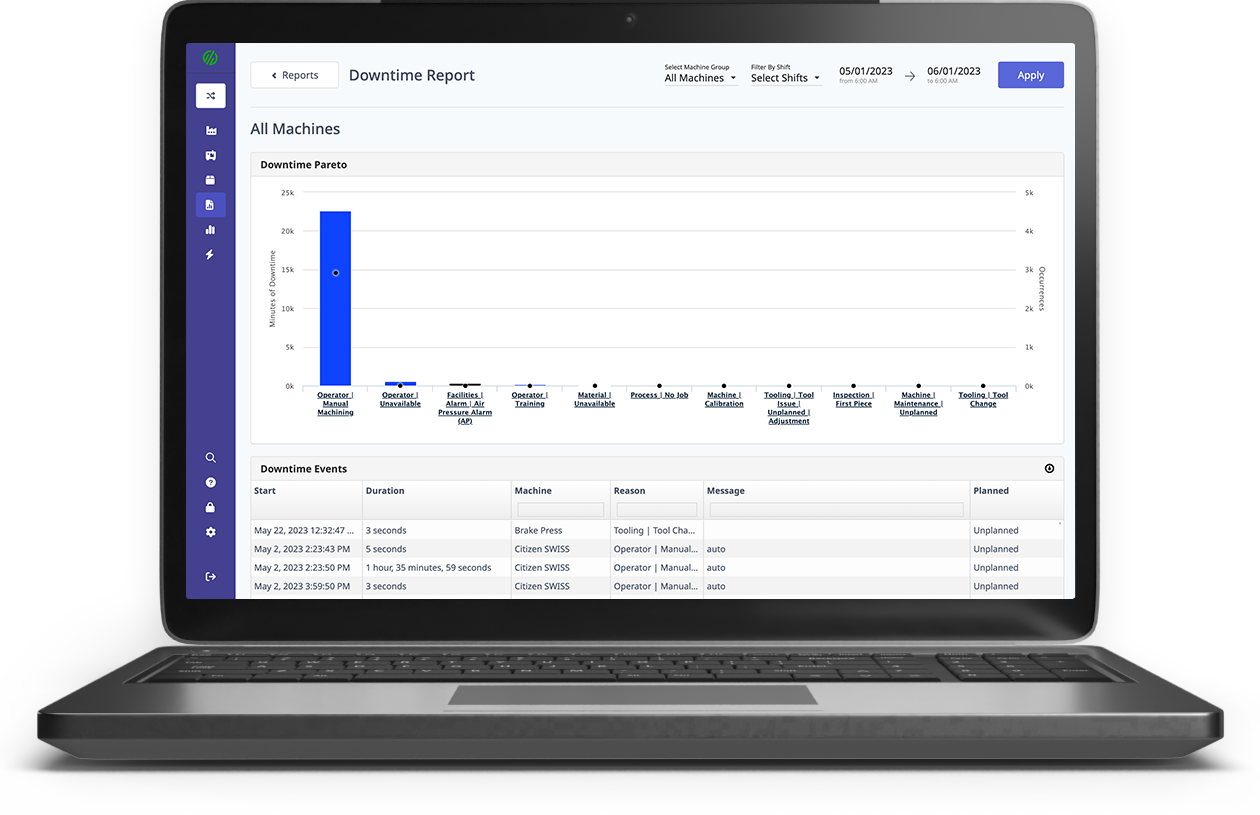
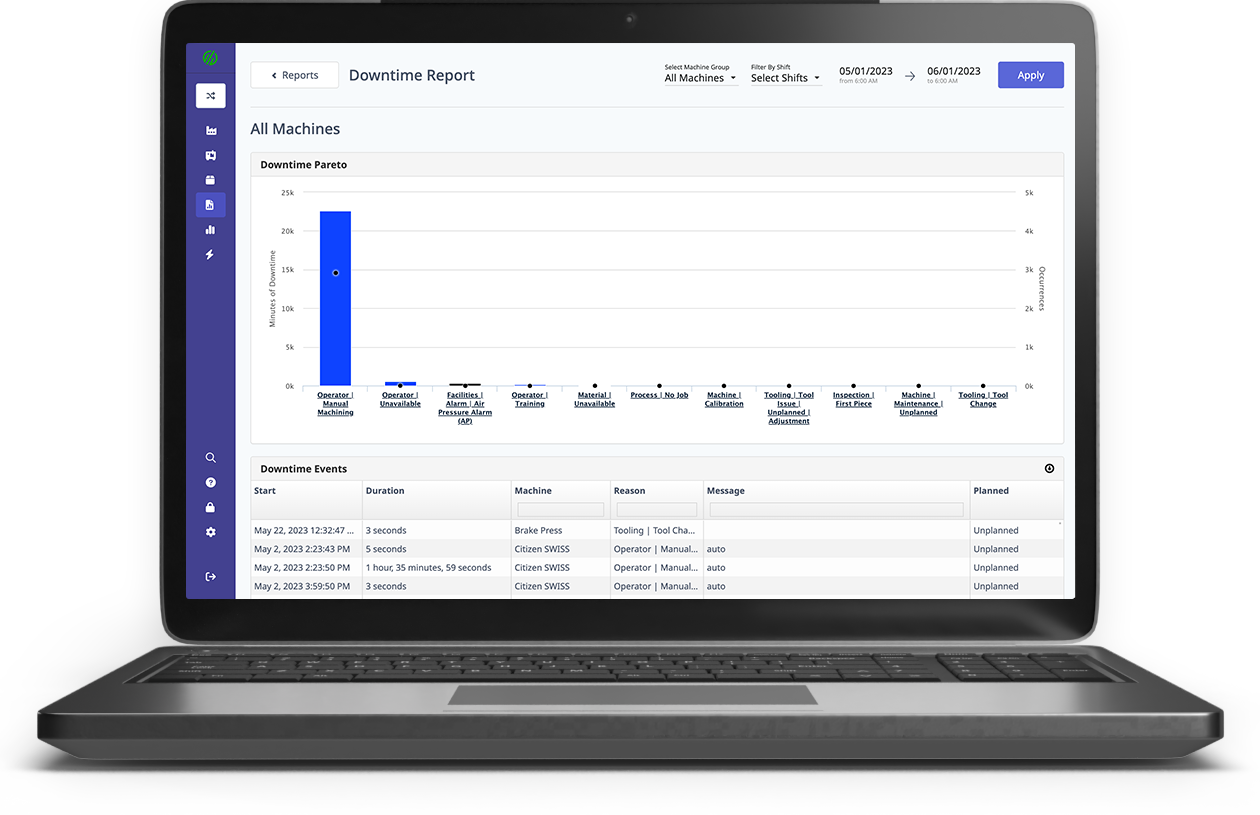
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)





Comments