Over the last decade, digital transformation has accelerated among all industries. This revolution of new technologies has altered traditional manufacturing and the business landscape across the globe and is poised to accelerate even more.
As recently as 2018, manufacturing companies transformed digitally accounted for $13.5 trillion of global GDP. But it’s estimated that by 2023, this number will have risen to encompass $53.3 trillion of global GDP.
This article will discuss digital transformation in manufacturing and look at some of the trends driving this revolution.
Digital Transformation in the Manufacturing Industry Today
Even before the pandemic began, the disruption and digital transformation of the supply chain were already underway. Smaller enterprises saw the new suite of technologies as a competitive advantage or a means to address a lack of valuable skill sets through automation.
On the other hand, larger enterprises struggled with adoption. A 2018 study by McKinsey found that businesses with 100 employees or less were 2.7 times more likely to adopt digital transformation successfully. And the same survey found that overall, under 30% of these transformations succeeded.
While the pace of digitization in manufacturing was steady but slow with many fits and starts, it was widely recognized by C-suite executives and CEOs as the future of business. But as the COVID-19 pandemic hit in 2020, many businesses were forced to speed up adoption and make it work as a matter of survival.
Others, equally threatened in their business models by a once-in-a-lifetime disruptive event, quickly began looking for ways to continue operations during the pandemic while ensuring the safety of their workers. Today, as the effects of COVID-19 slowly recede, a new reality has taken shape in manufacturing, with as high as 91% of all manufacturing operations stating that they’ve increased investment in digital transformation and will continue.
The Impact of Digital Transformation on Manufacturing
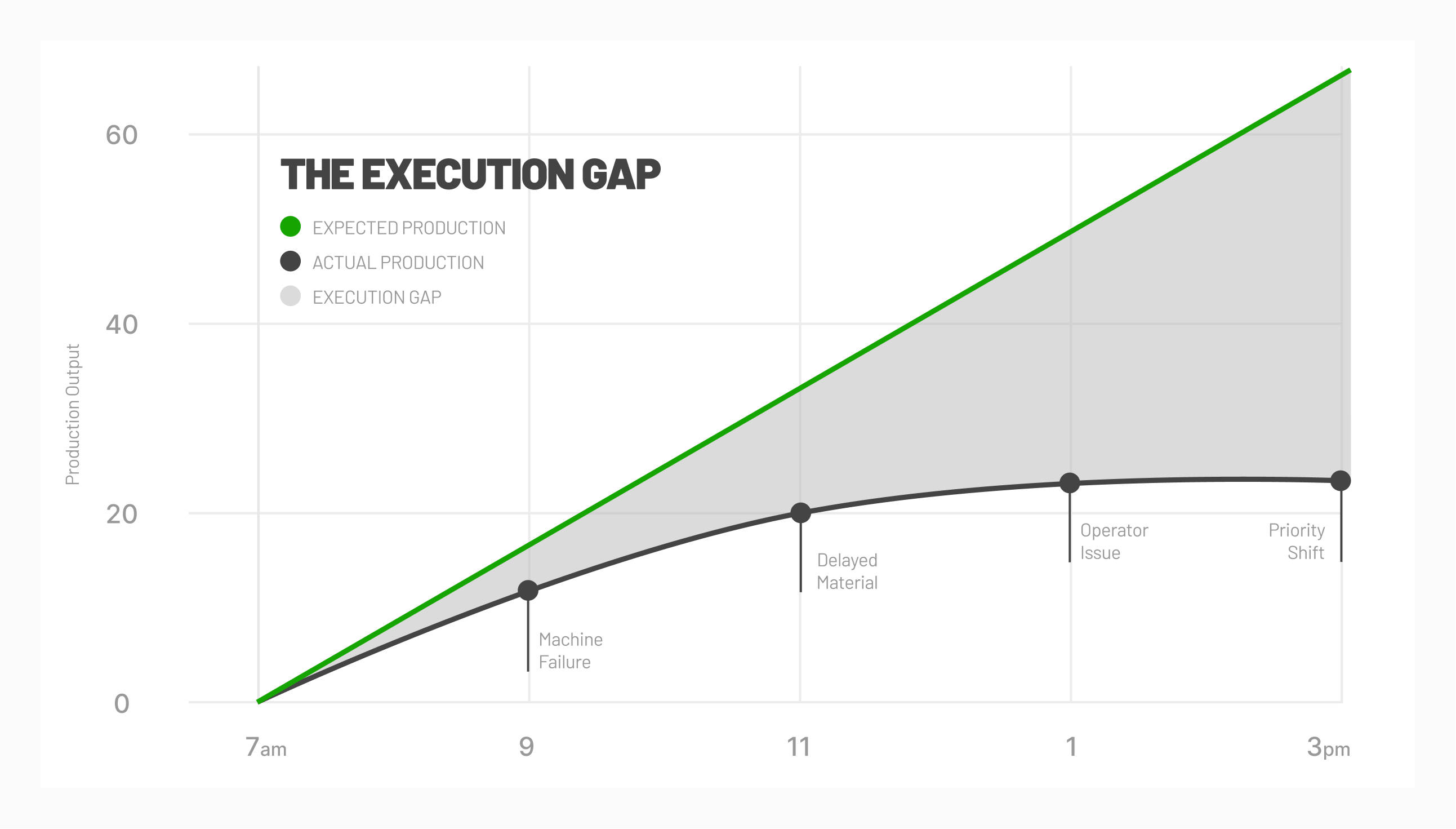
Digital transformation disproportionately impacts a manufacturing company compared to everyday data management or process improvement methodologies. More manufacturing processes are transformed by leveraging machine data using digital technologies.
A fully implemented digital transformation strategy transforms more than just manufacturing processes; it changes business practices throughout the enterprise. Predictive analytics may also improve inventory management, supply chain planning, and more.
As real-time data is used to improve manufacturing processes, the emerging technology framework drives equally real-time responses to business conditions and demand. As the framework matures, traditional manufacturing processes are transformed, and manufacturing companies operate more efficiently.
Challenges of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Despite the new urgency within the manufacturing sector, there are still challenges for adopters to overcome. These include:
Capital Expenditure
While small and medium-sized companies that were early adopters came out with a competitive advantage, it’s still true that many of these smaller firms lack the capital resources and deep pockets of larger competitors.
Companies of all sizes also tend to focus on ROI, and the formula for successful ROI is different for different-sized enterprises. There is also the problem of linking investment dollars to future profitability. Many companies struggle with the upfront cost, but the cost of not adopting may be higher or even fatal.
The solution may come through the modularity of many of these platforms. By using cloud-based software and cost-effective hardware, companies may develop incremental plans that focus on a critical area, such as downtime, with plans to scale the system as results pay for themselves through increased production.
Skill Sets
Many manufacturing industries find it challenging to discover that they must source and train people to deploy digital technology successfully. Platforms commonly run using AI and machine learning algorithms.
But other technologies, such as digital twins and 3D modeling, may be required depending on the industry. Retraining existing workers may not be possible. And these new skill sets are in high demand.
IT Issues
IT is especially challenged by the skillset issue as well. Expensive fiber-optics, servers, and long cable runs must now give way to cloud-based technology with different requirements.
IT is also tasked with transferring data, ensuring security and access, and a host of other tasks that are either unfamiliar or run contrary to what they’ve done traditionally. And many of the legacy systems in place may have extended software licenses of their own that are now obsolete or not needed for a new digital world.
Corporate Culture Issues
The manufacturing industry has always been seen as made up of predominantly manual workers. And while there will still be places within many industries for strictly manual labor, many new skills and training are required to bring operators to the technician's skill level.
These new technologies often utilize interactive screens, tablets, and other human-machine interfaces to input and receive data the operator needs. Training will need to be done to develop the skills for workers to understand and use these types of systems and leave behind paper-based ones.
Data Security
Many company executives who understand the importance of digital transformation and see its current and future benefits also worry about security. Most of these systems are cloud-based and operate over the internet. They may also have Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity and Ethernet to connect legacy analog equipment to the floor. These IoT security challenges do pose a risk but can be mitigated.
With news of hacks appearing almost weekly, many are worried that such an event could stop production. Others fear that in the case of critical industries such as pharmaceuticals, these incidents could be life-threatening. While these challenges are real, security protocols are growing and will continue to focus on heightened and tightened security as adoption accelerates.

5 Digital Transformation Terms and Trends in Manufacturing
Digital transformation is a group term that speaks to a collection of technologies and methods collectively reshaping manufacturing and creating new business models. Here is a look at some of the trends.
1. Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is a global term for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. It encompasses all the technologies that refer to data capture and exchange in manufacturing. Industry 4.0 also includes technologies such as the Industrial Internet of Things, cloud-based computing and systems, connected manufacturing environments, 3D printing (additive manufacturing), and all components that make up the combined cyber-physical system. It refers to all things combined or networked in a modern factory that make such businesses "smart" in utilizing technology to realize efficiency gains and optimized processes.
2. IIoT
IIoT stands for the Industrial Internet of Things and falls within the framework of Industry 4.0. IIoT is the collection of sensors, data collection devices, measurement systems, and actuators that encompass a smart factory. These systems are linked to powerful analytics that allow real-time visualization of the factory floor or shop floor and enable autonomous or semi-autonomous actions to be taken. It also will enable decision-makers and operators to act quickly on actionable insights provided by the analytics engines to gain greater efficiency and reduce downtime while improving the quality of products across the company.
3. Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning and AI are two different things that can work together within a machine data platform. Machine learning is a term that describes advanced algorithms that can change the way equipment is run or suggest prescriptive steps to improve. The greater the volume and quality of data the system receives, the better the quality of the prescriptions. AI, or artificial intelligence, is the advanced intelligence engine that allows autonomous or semi-autonomous actions by the equipment itself. This is safer and more efficient as the artificial intelligence applications can work at speed, replacing actions previously done only and more slowly by humans.
4. Predictive Maintenance
As machine learning and AI drive advanced analytics within a production monitoring system, the system obtains trends, insights, information, and other data. This allows for the development of predictive maintenance over preventive maintenance within the manufacturing industry and its operations. Predictive maintenance within a manufacturing industry uses actual machine state and part condition monitoring to determine failure points, send alerts, and make parts inventory decisions and staging occur at the optimum time to prevent downtime.
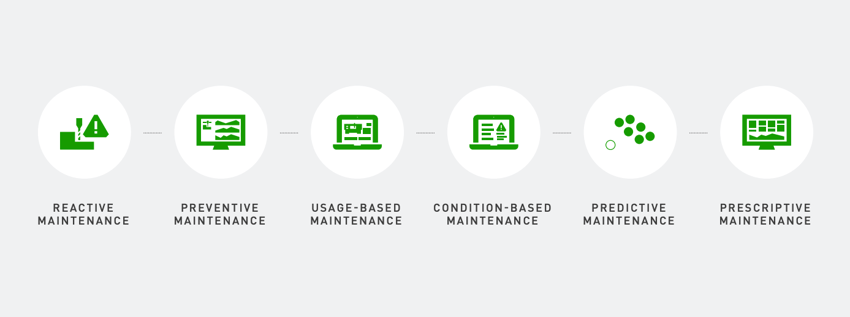
5. Robotics
Robotics isn’t used in every manufacturing industry. However, it’s becoming more and more common as digital technology advances. Robotics gets instructions from the platform's AI and machine learning elements which allows for safer, faster, more efficient, and more accurate production. Robotics allows manufacturing to occur at a speed that humans couldn’t manually achieve.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Companies that invest in digital transformation will realize better profits and higher efficiency than their competitors. Benefits to adopting digital transformation within manufacturing include:
Improved Efficiency
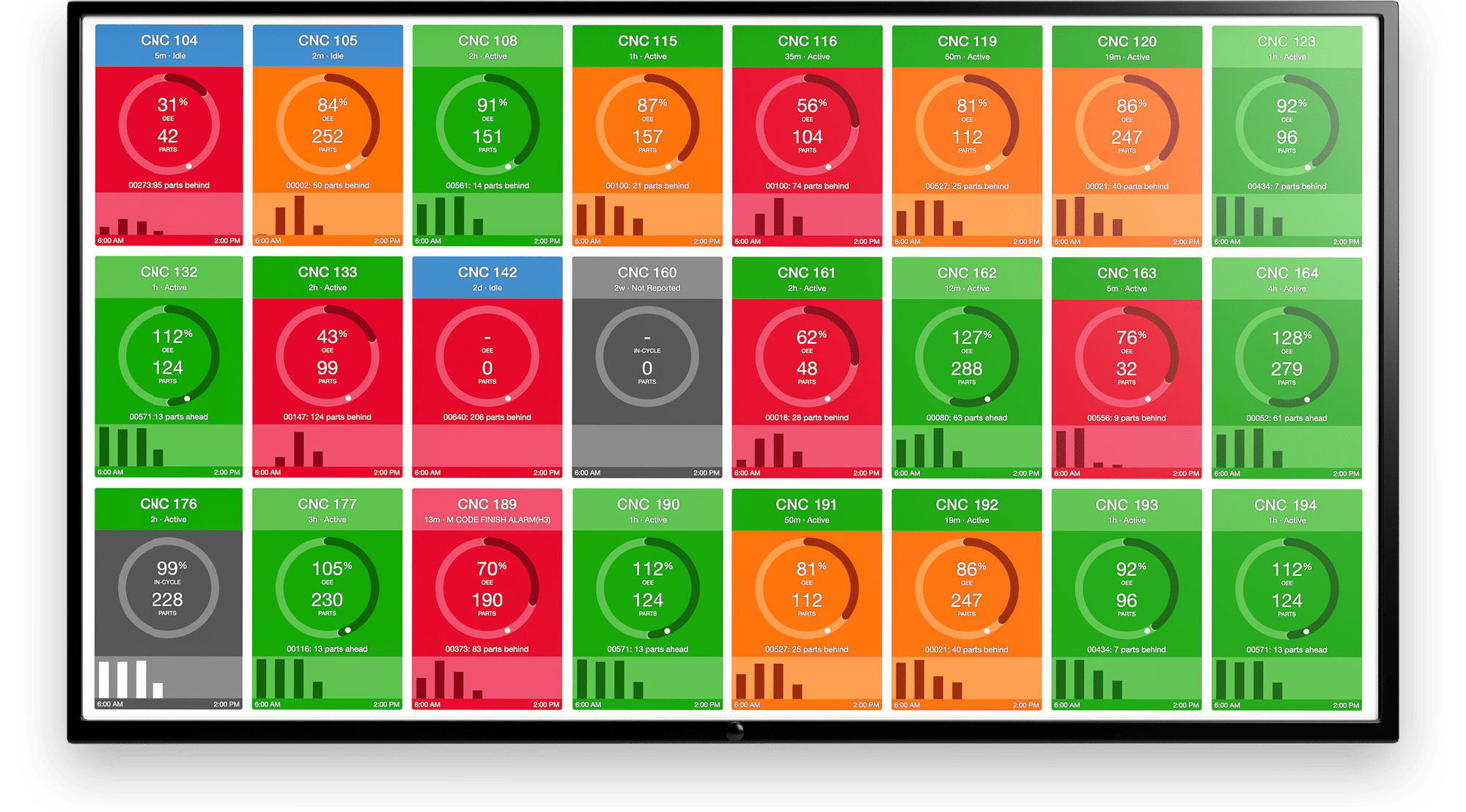
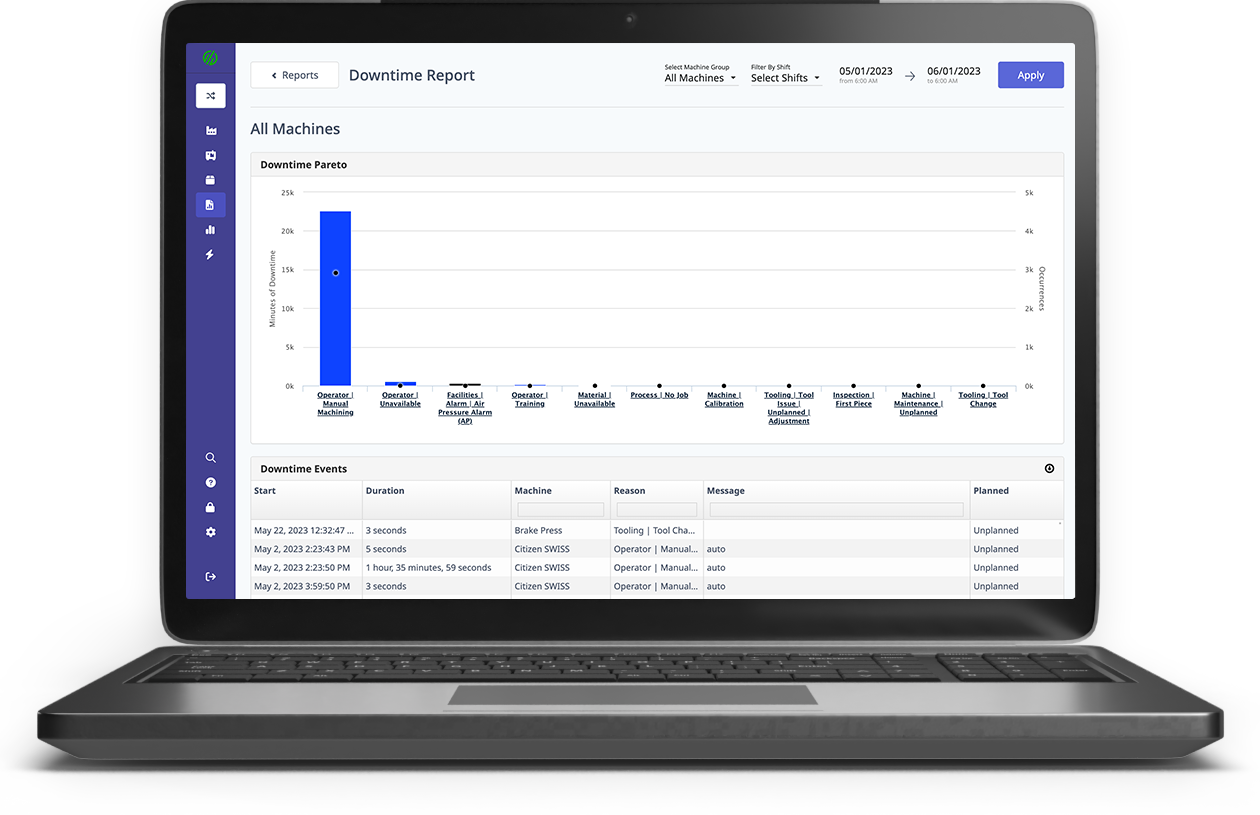
Companies that embrace digital transformation realize greater efficiency as downtime decreases. Platforms such as MachineMetrics production monitoring can immediately reduce downtime and enhance efficiency and equipment utilization.
Cost Savings
Higher equipment utilization and efficiency lead to reduced costs. Predictive maintenance can add to those lower costs with as high as 20% reductions in maintenance cost. And greater control over inventory and movement of materials within manufacturing can help control costs in the supply chain.
Optimized Processes
Using a machine data platform for production monitoring, such as the one available from MachineMetrics, can help optimize processes. This may take the form of new methods as well as ongoing and more accurate process improvement strategies based on real-time data.
Better Flexibility and Agility
In addition to AI and machine learning capabilities, platforms can be scaled and customized to reflect the needs of different equipment and industries. This allows for flexible and agile responses to changes and challenges.
Better Labor Utilization and Management
Digital technologies, such as machine data platforms, improve labor utilization and management across the company. A digital transformation journey uses machine data to automate processes and reduce labor, which is especially valuable in companies already facing skilled labor shortages.
Real-time machine data eliminates the need for manual data collection, sorting, entry, and analysis. This allows more value-added tasks per labor hour, reducing costs and addressing labor shortages using digital capabilities.
Advanced technology driving digital transformation also improves labor utilization and production management. With actionable insights from real-time analytics, managers can make more informed decisions. They can direct labor to where it’s most needed, develop improved training protocols, and design additional process improvements to squeeze the most out of every labor dollar.
Resilient Supply Chains
Few fields have suffered from disruption as much as supply chain management. Digital transformation allows managers to create complete end-to-end visibility in supply chain functions, as machine data is available to planners and legacy enterprise software in real time. It also enables supply chain professionals to develop supply chain strategies in response to disruption.
Planners can automate purchase strategies and ensure accurate min/max inventory levels based on current, historical, and future demand. As conditions on the production floor change, an advanced machine data platform will drive actionable data through the supply chain.
Better Product Development
As part of the fourth industrial revolution, advanced technology and smart manufacturing have the power to drive innovation and improve the cost of product development. They help manufacturers produce better versions of existing products and new offerings based on demand.
Digital twin technology based on real-time performance reduces entry costs for new products and serves to improve existing ones. Data-driven insights from production help sales and marketing teams develop new markets, products, and services based on the most efficient and popular lines.
Mass Customization
Consumers and B2B purchasers have higher expectations than in the past. A digital transformation can help a company cater to these expectations.
Digital manufacturing drives the flexibility of processes on an unprecedented scale. The digital transformation process allows industrial manufacturers to deploy previously unavailable strategies, including concepts like "lot size of one" and mass customization of traditional product lines.
Time for Digital Transformation
If you’re looking for digital transformation, now is the time to jump in. With unprecedented disruption, manufacturers need the most advanced tools and best-in-class software to stay competitive. They should look to build an ecosystem of solutions that support rapid and continuous value achievement.
The foundation of a manufacturer's tech stack should be a machine data platform that can enable the autonomous collection, contextualization, and standardization of production data, as well as drive actionability on data to identify and resolve operational inefficiencies.
Learn how MachineMetrics enables digital transformation for manufacturers or book a demo to discover valuable use cases today.
Want to See the Platform in Action?
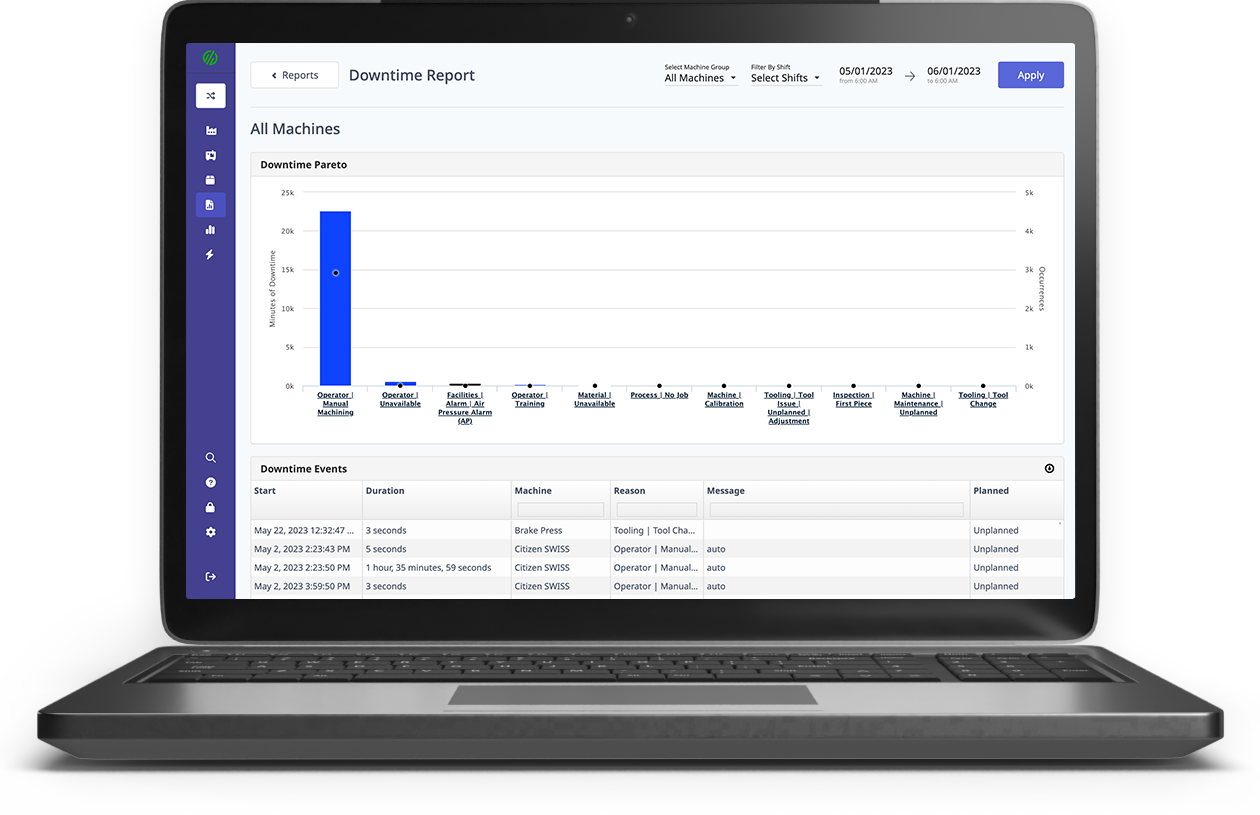
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)



.gif)






Comments