The rise of industrial data platforms has been spurred by the growing use of IoT in the manufacturing industry. These huge volumes of disparate data types and sources have encouraged manufacturers to implement platforms to collect and standardize data across their many machines and systems.
In doing so, these "Industrial Data Platforms" enable greater operational efficiency, complete production visibility, and help to drive continuous improvement initiatives.
But what exactly are these platforms, how were they developed, and what is their expected impact on the manufacturing industry?
What is an Industrial Data Platform?
Industrial Data Platforms collect, standardize, contextualize, store, and make accessible data from equipment and systems in an industrial environment.
Manufacturing companies have used MRP and MES systems for decades. But with the rise of the Industrial Internet of Things, advanced analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and edge devices, the amount of data has increased exponentially, along with new capabilities for analysis. This explosion resulted in the need for a multi-solution approach to process, store, and analyze the vast quantity of data and deliver real-time insights to end-users.
An industrial data platform consists of data collection, standardization, contextualization, storage, and delivery. By running solutions at or near the edge, data can be organized, cleansed, and partially structured before being sent to the cloud. The result is a more streamlined data management system with greater efficiency. This two-way road combines multiple technologies, so a company’s end-to-end needs are met for data management.
How Did the Need for Industrial Data Platforms Develop?
The rise of data as a valuable commodity has presented some problems in recent years. Technologies became overwhelmed, resulting in fragmented and siloed databases.
For example, while data acquisition was nearly instantaneous, it often resided in numerous databases spread across an enterprise. To add to the confusion, these databases were often managed by various service providers, creating a latency or interoperability problem - one of the things IIoT and Industry 4.0 technology were designed to eliminate.
Data managers realized the need for a consolidated and tiered structure where all databases, communication, connectivity, and analysis resided in one place. This consolidation would prevent siloing of data and ensure all collected data was available for predictive and descriptive analytics. It would also allow for better corporate governance of data and better collaboration among users.
Industrial Data Platform Requirements
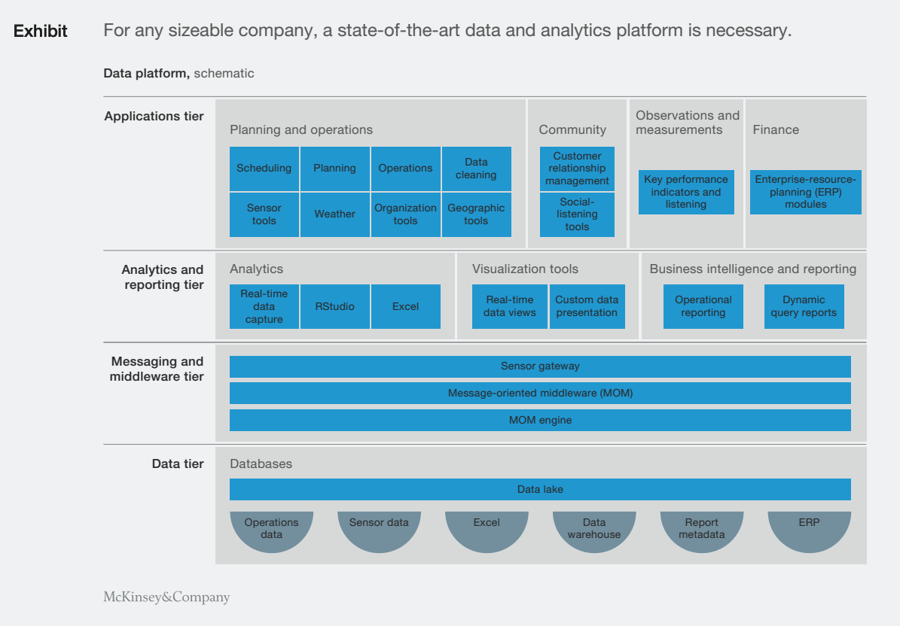
One McKinsey analysis suggests that a state-of-the-art industrial data platform with advanced analytics be built with the following tiers:
- Applications Tier: Scheduling, sensors, planning, operations, CRM, KPIs
- Analytics and Reporting Tier: Real-time data capture, real-time data viewing, and customized viewing applications, BI reporting
- Messaging and Middleware Tier: Sensor Gateway, MOM engine
- Data Tier: Operations, sensor data, data warehouse, metadata, ERP system
There are some critical requirements for any industrial data platform, including:
Integration and Connectivity
Any industrial data platform will require flexible and reliable connectivity.
There are hundreds of solutions in the market that utilize traditional device connectivity over cable and T1 lines. There are also many device providers that use Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity.
MachineMetrics, for example, specializes in the connection and collection of machine data. Our flexible system allows device connectivity over OEM equipment with direct machine integrations, sensors, and IoT devices, retrofitting of automated equipment, and even the connection of analog devices.
This enables machine connectivity to any make and model of equipment, ensuring that manufacturers can collect, standardize, and contextualize all of their machine data.
This then enables the data to be used in other systems that require accurate production data to carry out their core functionality, like a CMMS or an MES.
Integration with other devices, data sources, and processes is important as well. The more agnostic the connectivity and device solution, the larger the ecosystem and the greater the data acquisition.
The ability to integrate and analyze quality data from analog equipment alongside data acquired from OEM embedded devices means that data streaming to the industrial data platform is available for advanced analytics.
The ability to process or partially process data at the edge means that both batch and stream data are more easily integrated into the data platform. This reduces latency and allows platform analytics to spend less time cleaning, processing, and organizing data.
Helpful Read: Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing in Manufacturing
Data Standardization and Contextualization
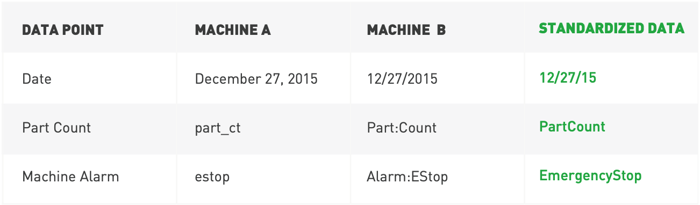
Data is at the heart of any industrial data platform. As such, the way it’s prepared is critical. Data platforms need standardized data to devote more processing power to analytics and predictive and descriptive insights.
The MachineMetrics Machine Data platform, for example, uses an automated data transformation engine to turn machine and equipment data into standard data structures. This helps empower more consistent reporting and analytics. Standardized data is useful in custom sensor data, machine state, alarms, overrides, diagnostics, speed, and machine modes.
Standardized data can be more readily analyzed where predictive and prescriptive solutions can be added. This contextualization of the data is one of the most significant promises of IIoT, enabling a host of options on the shop floor and at the manufacturing level. Contextualized data uses pre-configured actions to perform tasks without human intervention, resulting in reduced downtime.
Still confused about the Industrial Internet of Things? Read our full guide on IIoT.
Scalability
The ability to easily connect to an industrial data platform is critical. But any advanced platform should also be scalable.
In many companies, manufacturing data comes from a wide array of equipment. Sometimes this equipment is purchased from different OEMs. Other times, a factory may consist of multiple processing steps and require different equipment. There are also countless companies using equipment across generations - from analog equipment to devices with IoT capability embedded.
An industrial data platform must accommodate inputs from all these sources and grow as the business grows. Having fully integrated devices and standardized data allows for easier scaling as more machine assets are added to the platform.
Extensibility
Traditional manufacturing software was often fragmented, siloed, and suffered from a lack of interoperability. The ability to capture, prepare, and analyze data in real-time drives significant value.
A platform must be fully extensible for its analytical capabilities to be used by data from other software systems within the enterprise, such as a CMMS. Platforms such as MachineMetrics offer an extensible platform to connect via API to many legacy systems, including MES ad ERP.
But with MachineMetrics, extensibility goes beyond API connectivity. The platform allows extensibility with edge devices to reduce latency and partially process or analyze data at the machine level. This extends the value of data while making system resource use more efficient. Operators can rely on real-time insights to optimize processes.
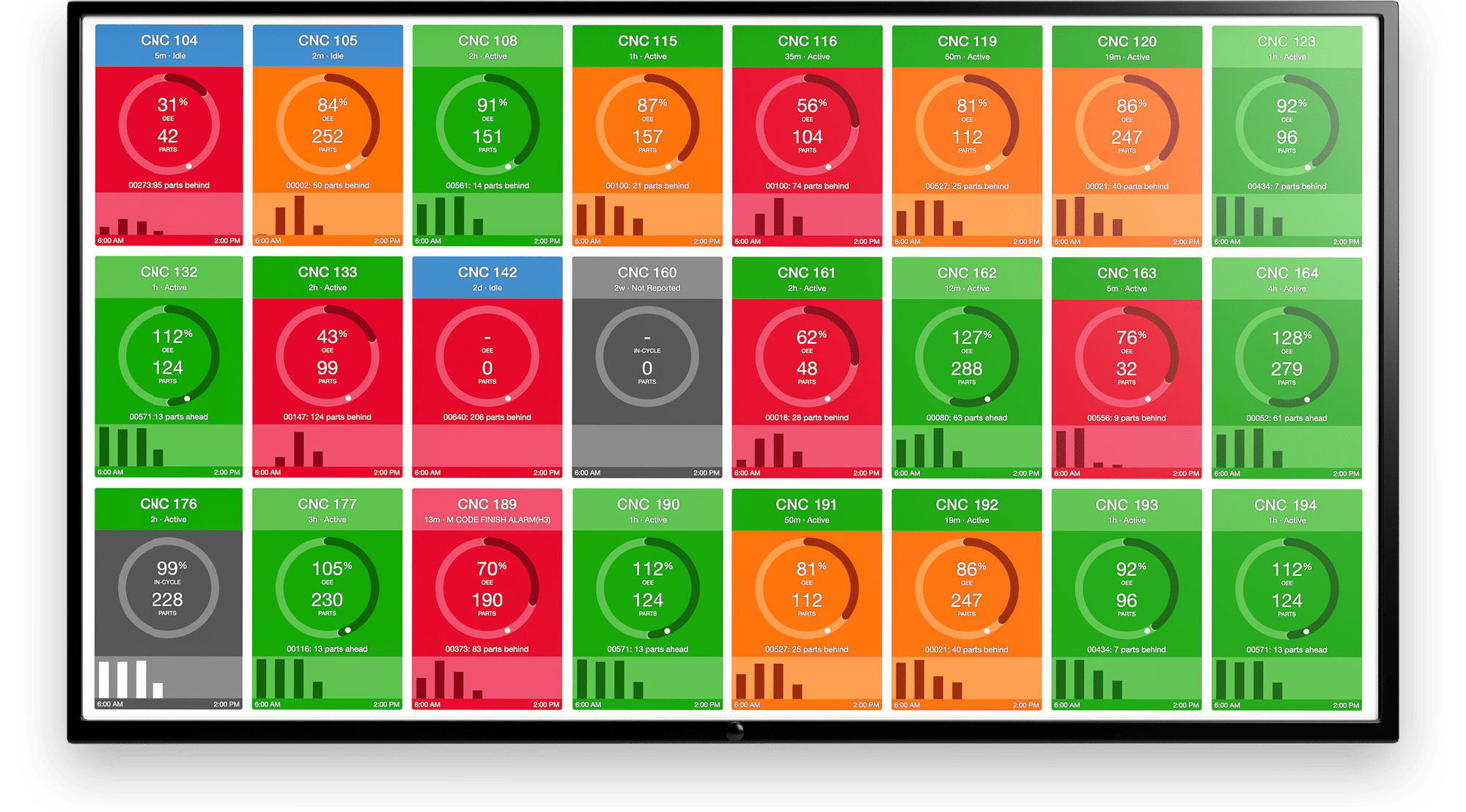
Data reach is also extended through intuitive, customizable operator interfaces. Technicians, operators, and managers have access to rich visualizations where they’re needed most. They can add their own insights and see machine status displayed by the spindle, machine, or factory level.
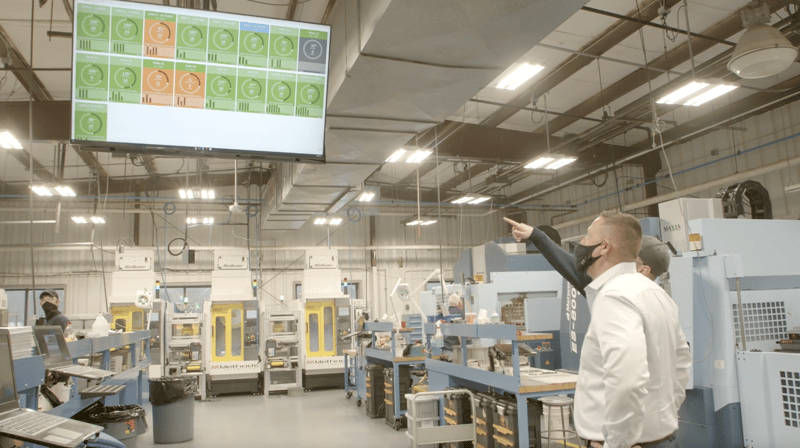

Advantages of an Industrial Data Platform
There are several advantages of using an industrial data platform. They include:
- Consolidated Data: In a data platform, data is consolidated in one place in the cloud. This consolidation means all databases can use the same service to render insights and suggest business strategies and process optimization.
- Improved Access: Because data assets are housed under a single service provider and use the same analytics engines, users can quickly and easily access data from the production floor. The value of HMIs, mobile tablets, phones, and PCs mean that decision-making is faster and data-driven.
- Valuable Applications: Because data operations are tiered within the platform, users have access to customizable reporting and real-time KPIs. They also have the ability to zoom in to view specific machines and spindles or zoom out to view overall factory performance.
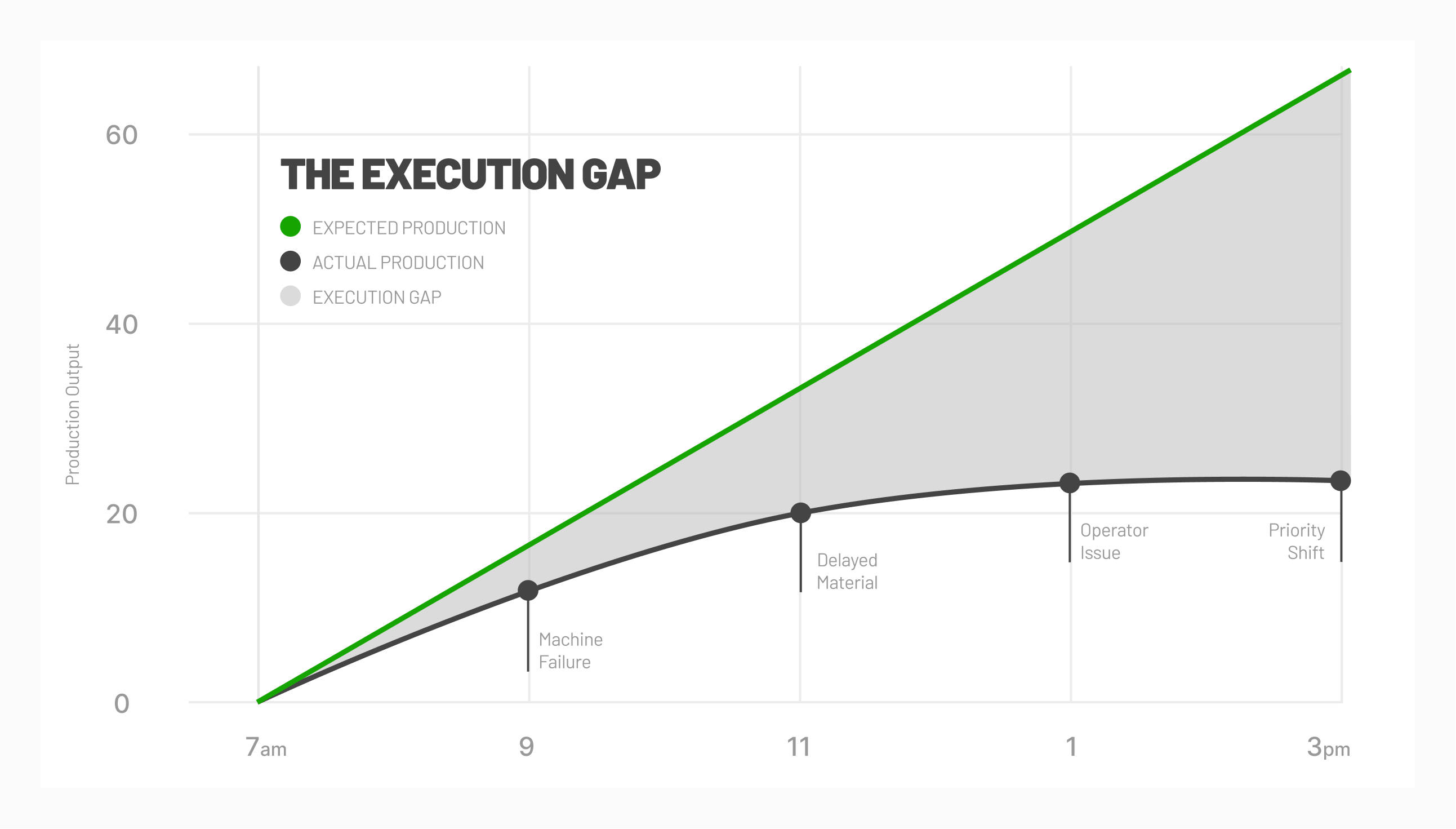
- Improved Operations: The real-time analysis of machine conditions can lead to new strategies within management, as well as enable automation. For example, predictive maintenance programs using actual machine performance and conditions can significantly lower maintenance costs and reduce downtime.
- Higher Security: Many companies risk security with ad hoc and fragmented IoT devices and software. Integrated solutions mean that even though IoT devices may lack full security, the data platform can significantly manage security through authentication and device authorization. This lowers the risk of a successful attack.
- Reduced Costs: Since IoT devices and deep data analytics use real-time monitoring, they can automate or semi-automate many processes. This automation reduces labor, unlocks capacity, lowers the number of variables and manual tests required for quality checks, and optimizes maintenance strategies. A platform with integrated solutions leads to optimized processes, higher productivity, and less waste.
How Influential Will Industrial Data Platforms Be?
It’s estimated that over 175 zettabytes of usable data will be generated by 2025. Industrial data platforms won’t only be influential; they’ll also become essential. They’ll create shared data in many industries with unique data and analytical needs.
Right now, most manufacturers are reliant on legacy MES and ERP systems to manage their operations, but these solutions struggle with data collection. We see this market rapidly change as larger players attempt to add on solutions to enable device connectivity, and new entrants offer simply point solutions for tracking just the bare minimum.
MachineMetrics was specifically designed to collect machine data and enable actionability. MachineMetrics integrates data, devices, software, and analysis in one powerful solution. Real-time analytics deliver actionable insights while you keep total control over your data. To find out how our platform can give you a competitive edge, book a demo today.
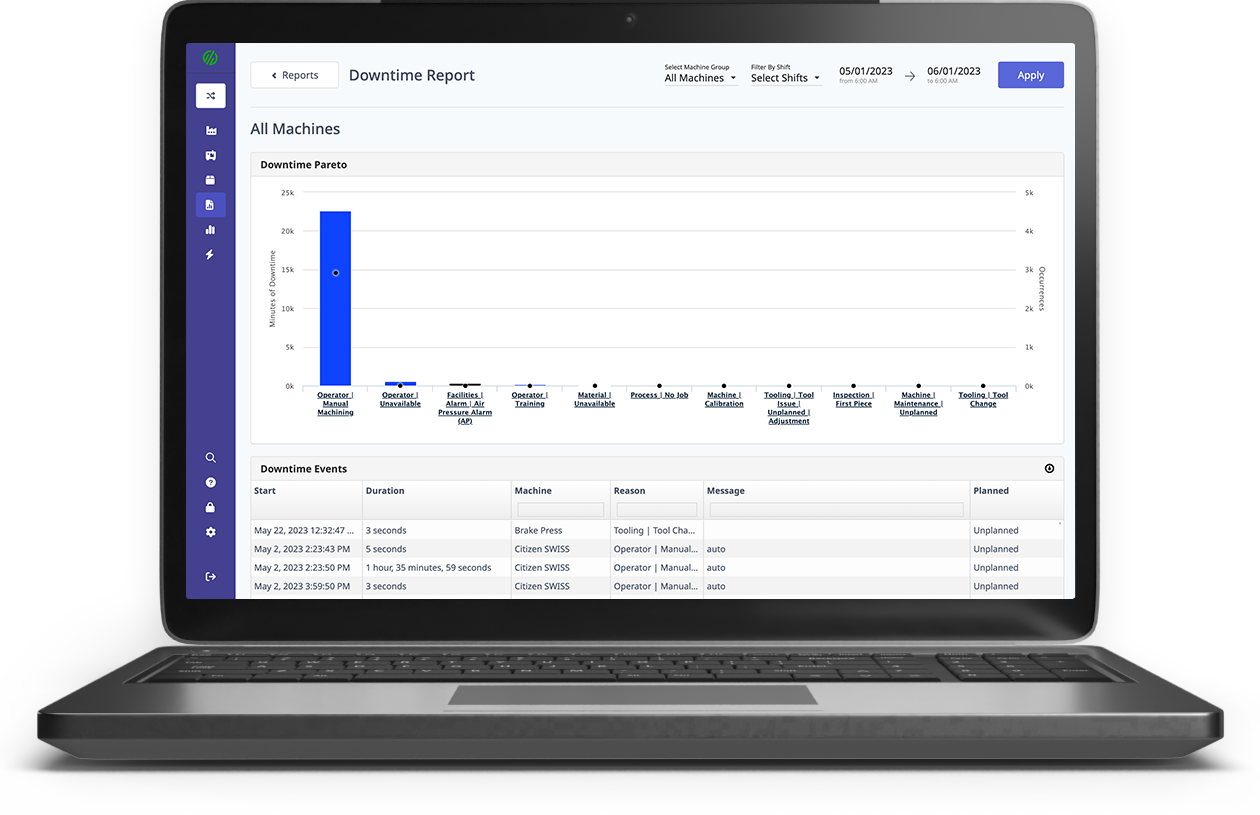
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)





.gif)






Comments